Before you proceed with reading this guide, it is recommended to have a basic understanding of CI and its common usage in development. If you are already familiar with these concepts, feel free to move on to the next section.
Codemagic
Codemagic is a user-friendly CI/CD platform designed to simplify and automate the build, test, and release processes for iOS and Android apps. It integrates with popular version control systems, enables automated testing, and facilitates seamless app distribution. Whether you're an individual developer or part of a team, Codemagic helps streamline your app development workflow for increased productivity.
Here's a guide how to use this tool to quickly set up CI for your project.
Requirements
In order to follow this guide and initiate the CI setup process, you first need to have a Flutter application that you will be configuring for CI. In addition, the source code for this application should be located in a remote GitHub repository.
Registration
If you are already registered, you can skip this step and go to the next one.
We recommend registering with the hosting account where you store the project (GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket), however registration is also available via email+password.
To sign in/up, go to this link.
We recommend that you skip the onboarding as everything that is offered there will be done later in this guide.
Adding Application
If you have not previously added CI to your applications in Codemagic, you will see this screen:
If you have already added apps, the app listing page will look like this:
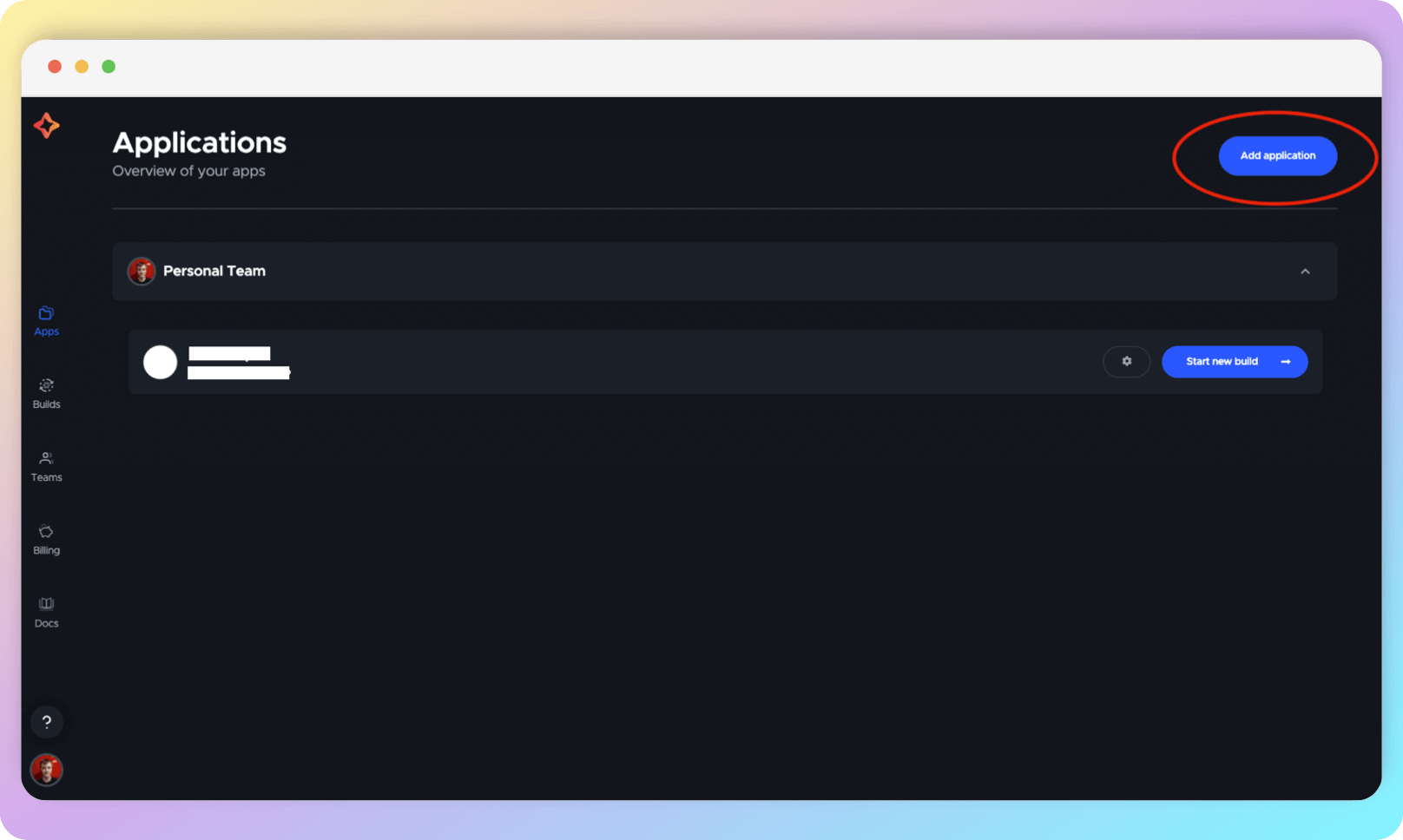
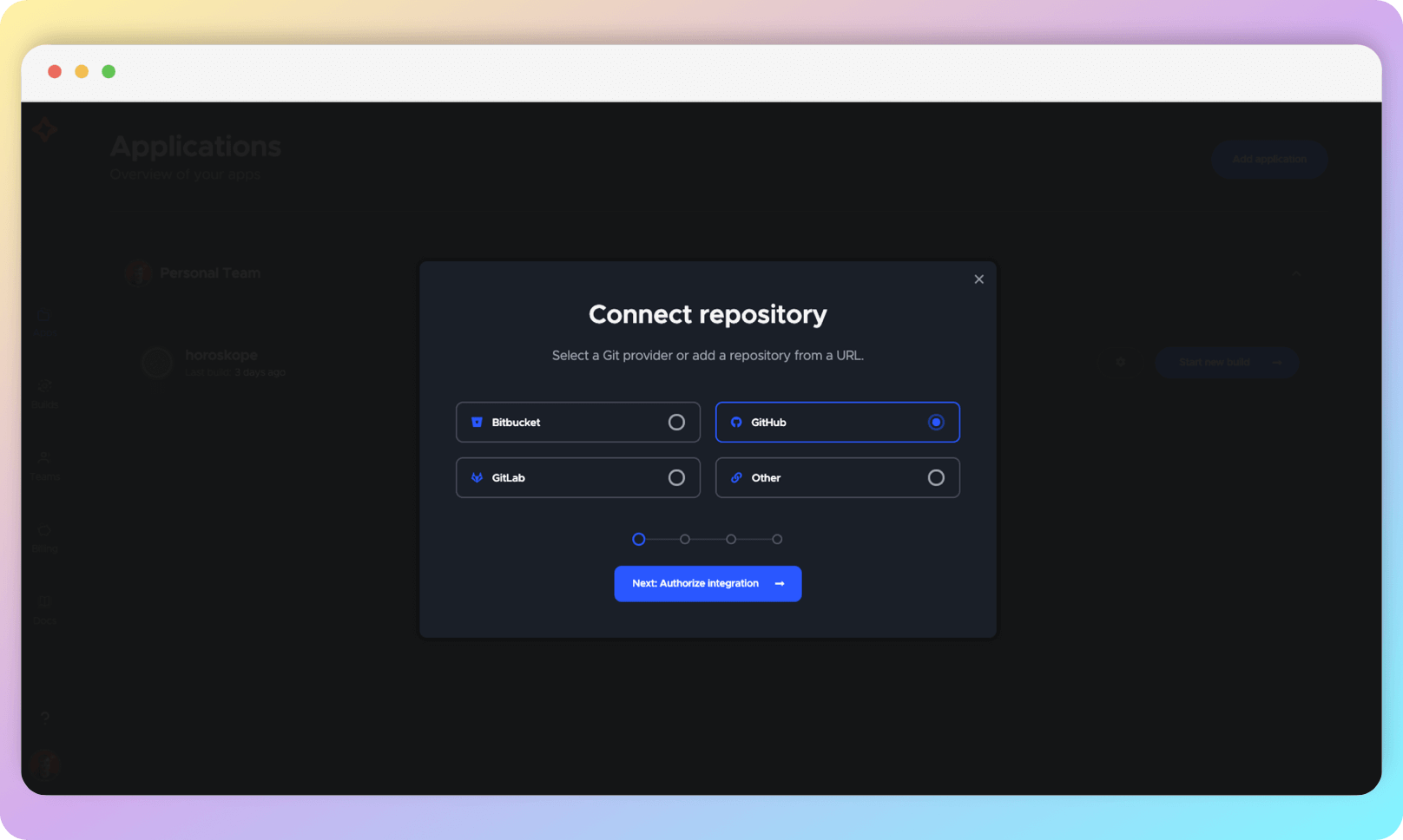
Select the hosting where your project code is stored (the differences will be minor, but in this guide we will deal with GitHub).
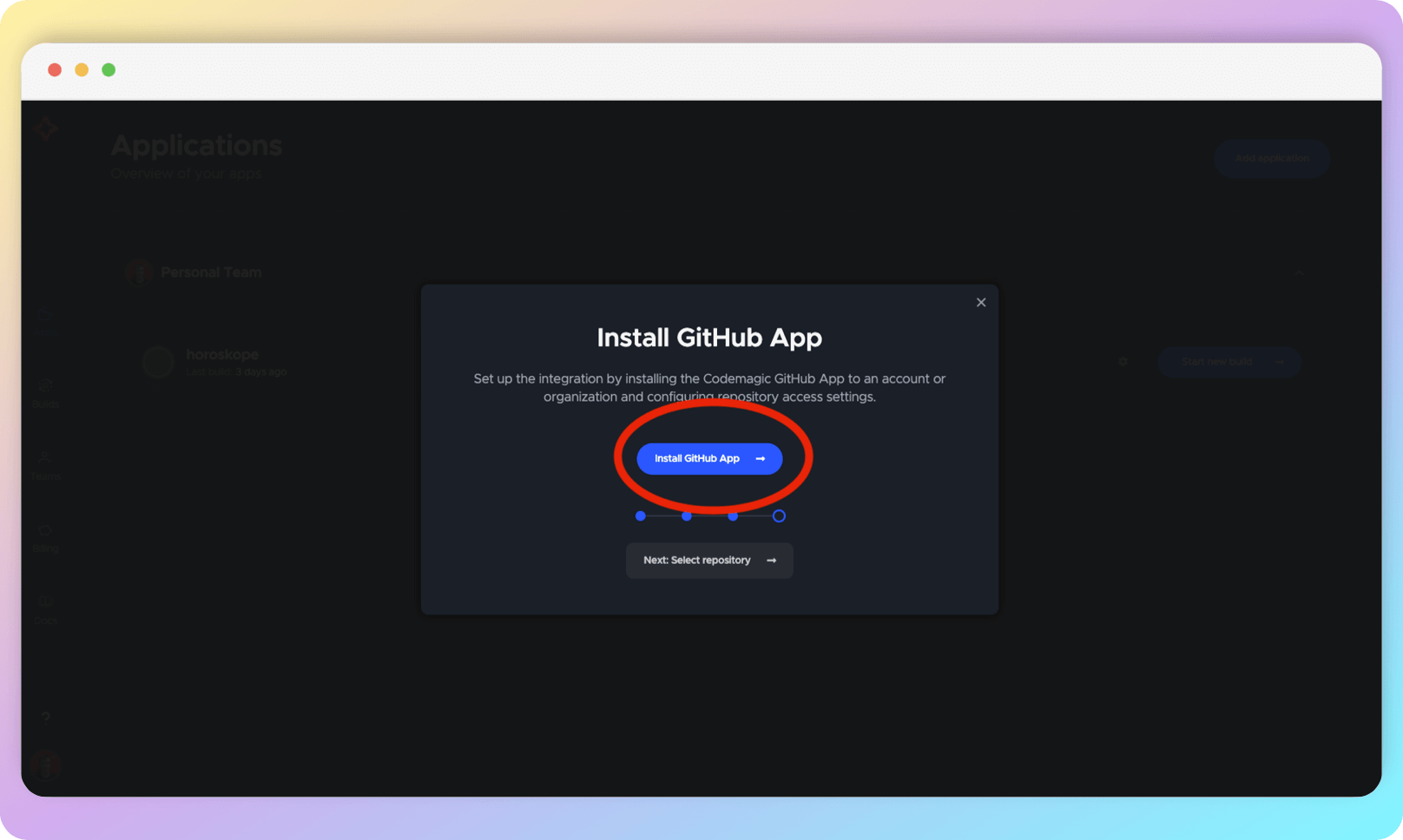
You will be taken to a GitHub page where you will need to select the organization that owns the project you want to set up CI for.
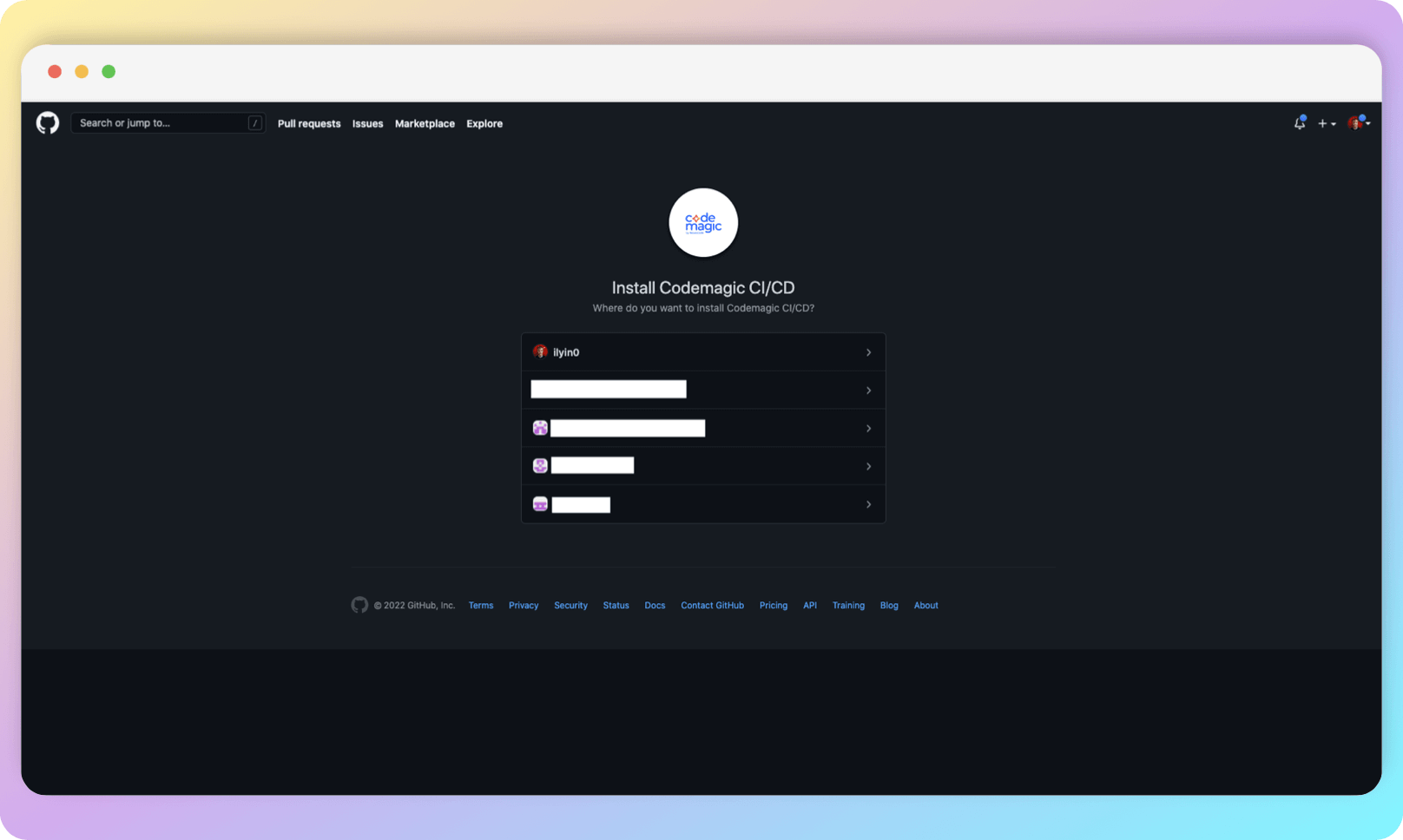
Then select the repositories you want to authorize Codemagic for. These settings can be edited later, so don't worry about selecting all the repositories at once.
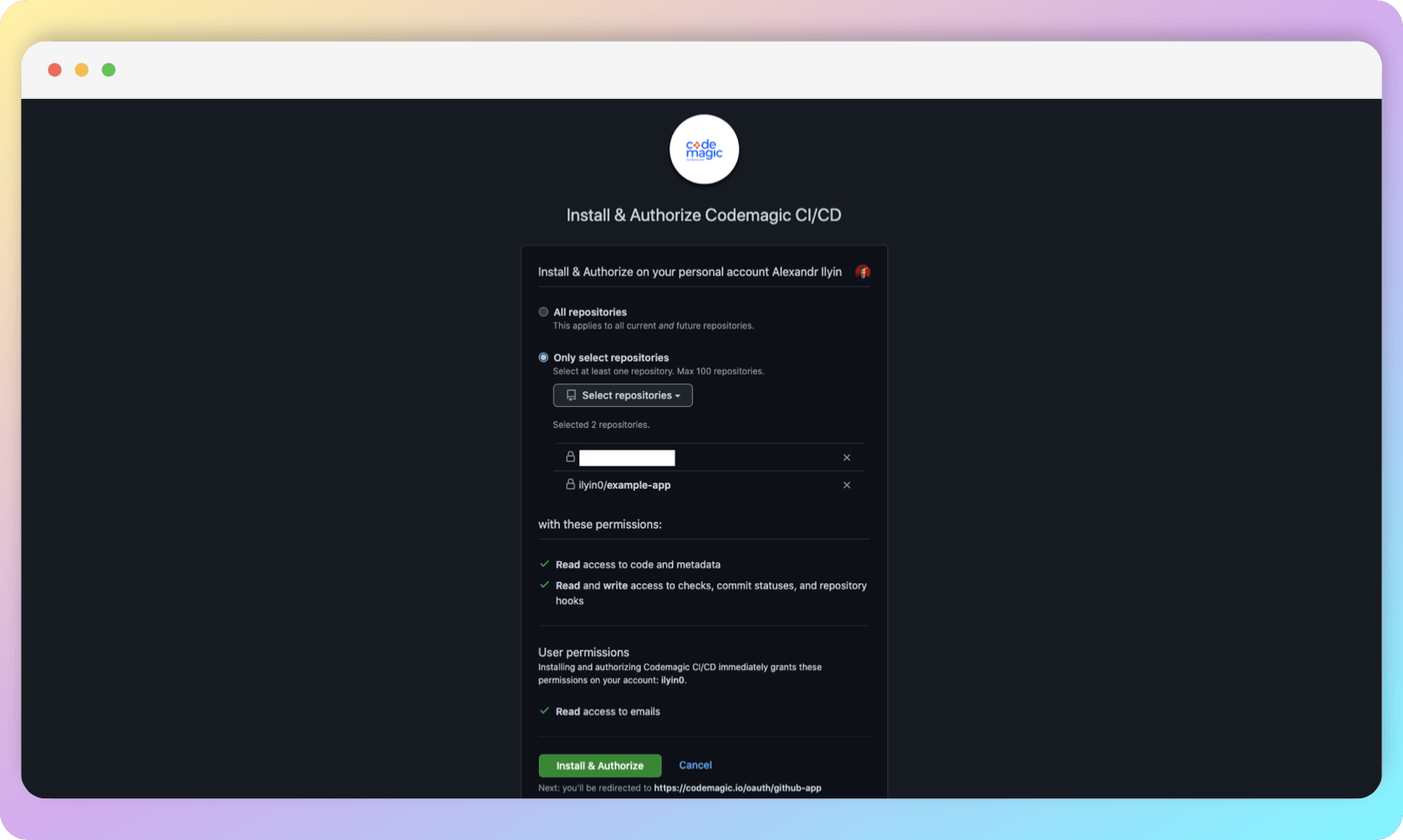
Take the next step by selecting your project on the Codemagic platform.
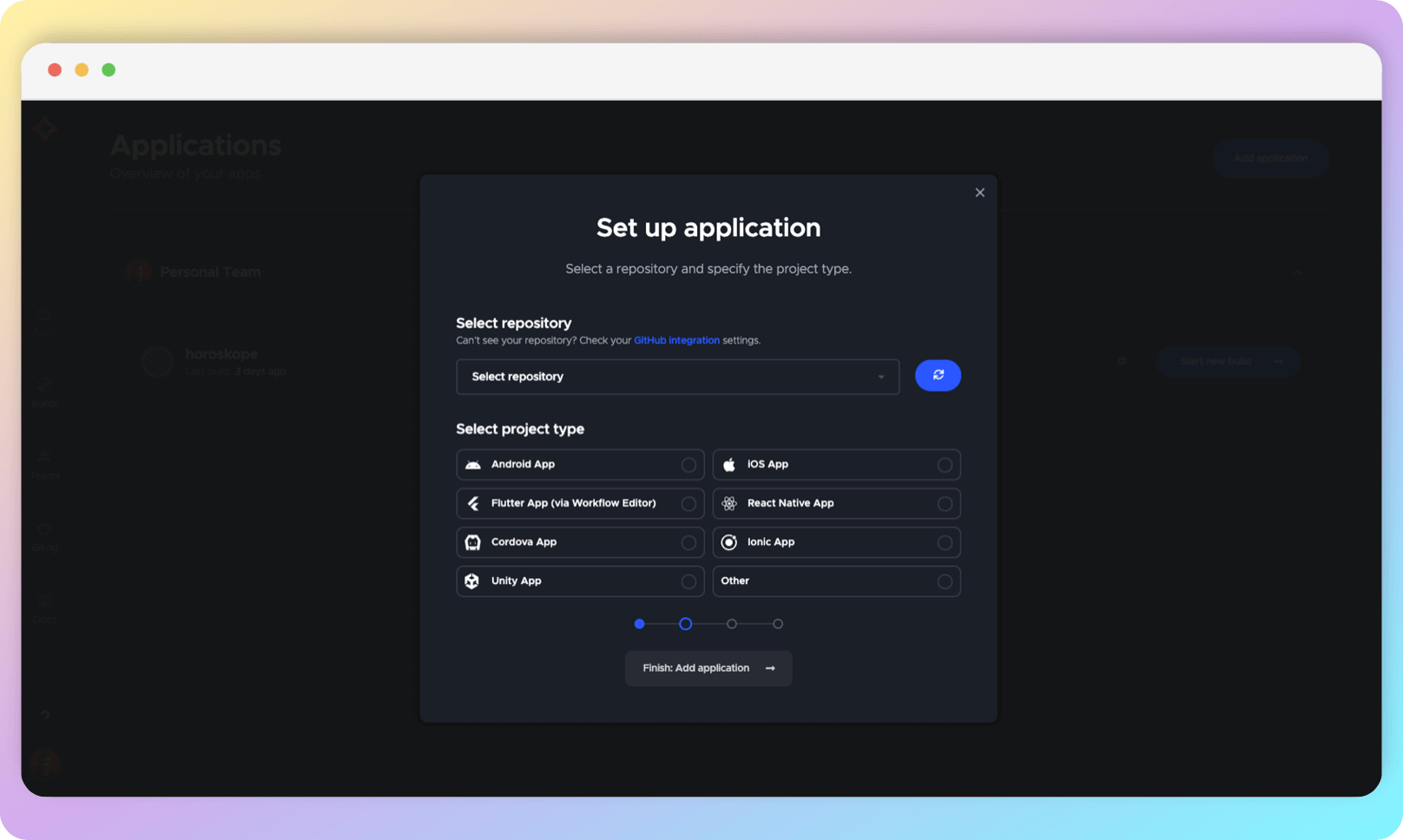
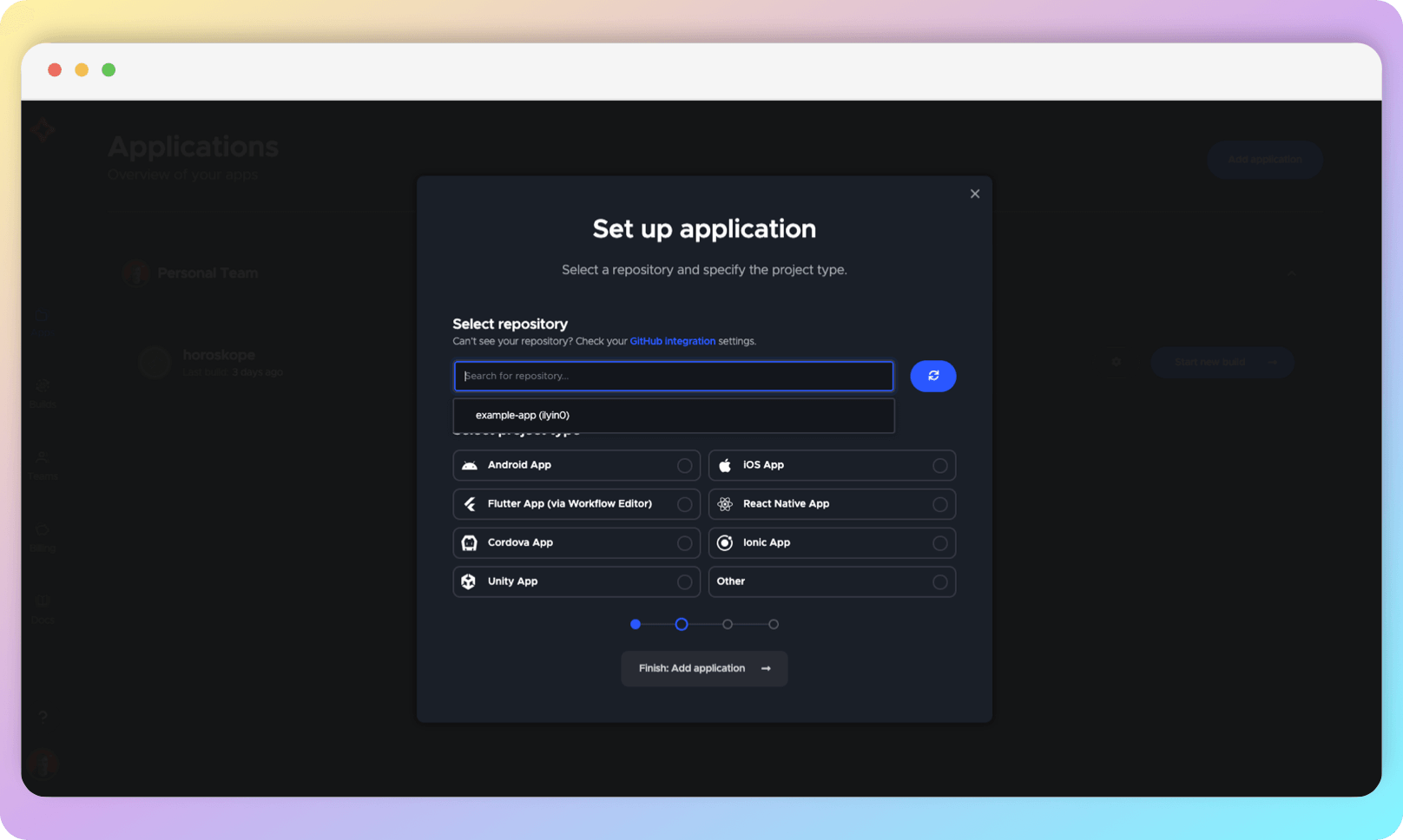
All authorized repositories will appear in the dropdown list. If yours does not appear, please refresh the list a few times until it appears. Then, select your repository.
In the section Select project type, choose Flutter App (via Workflow Editor) and click Finish: Add application.
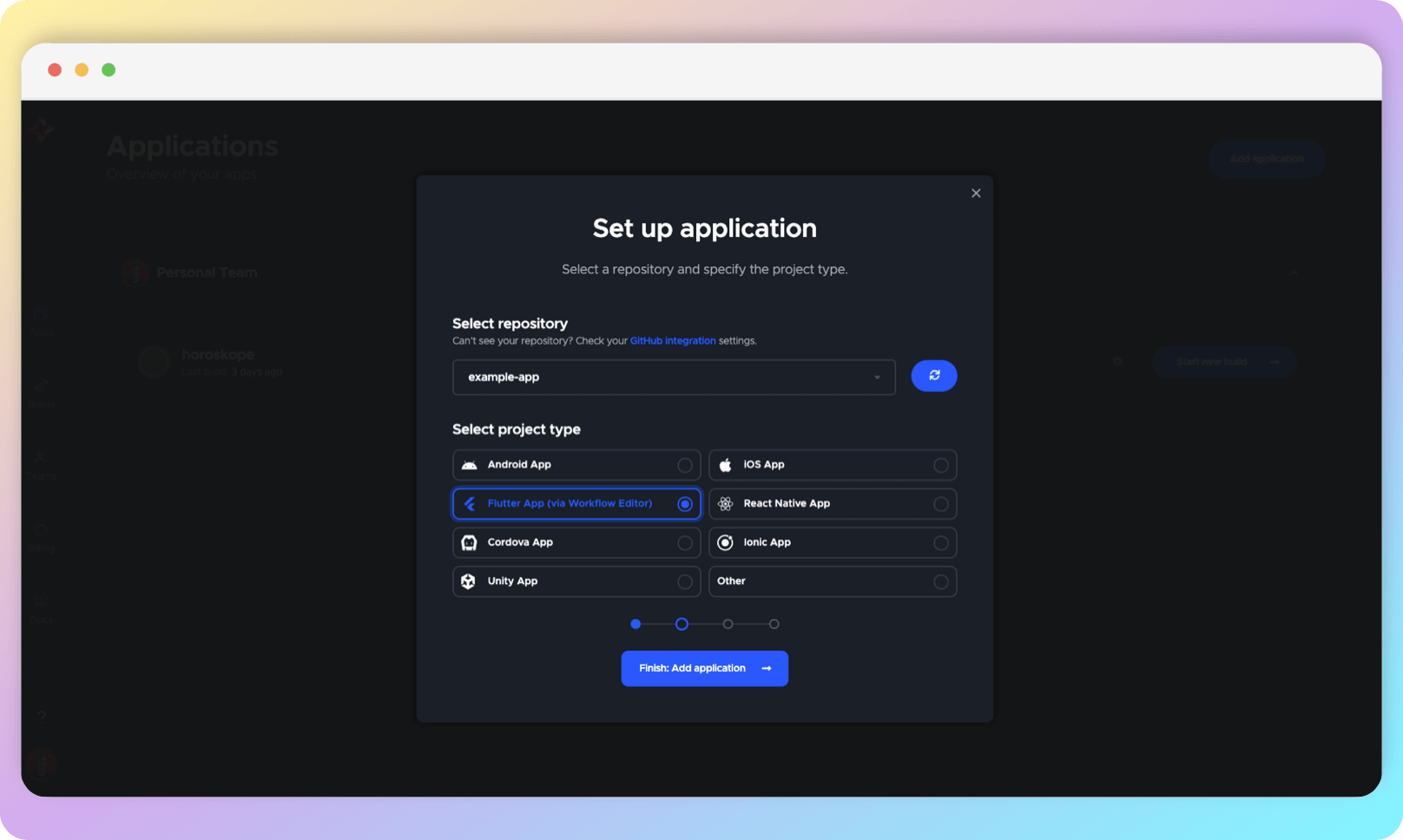
You will be taken to the workflow settings screen.
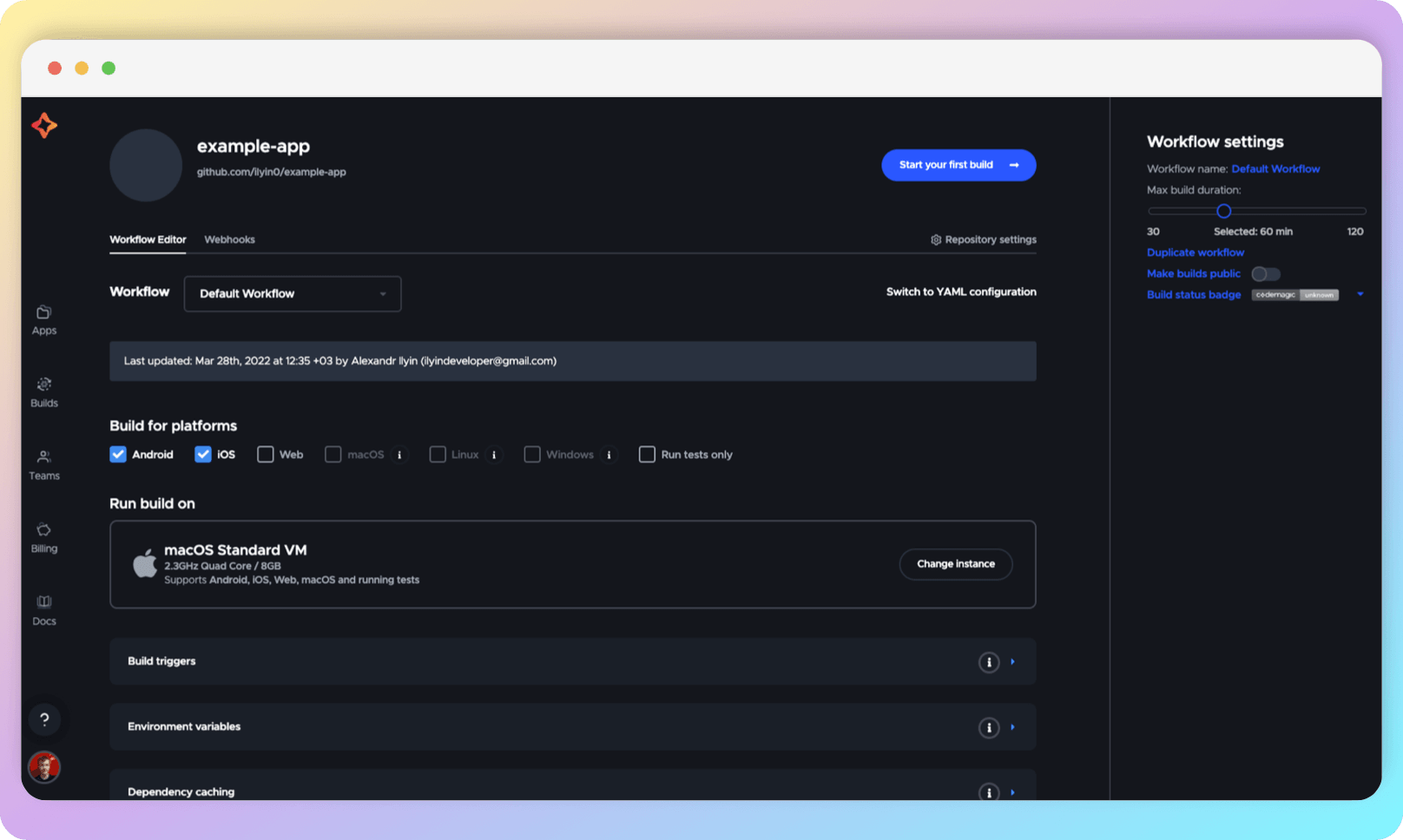
Workflow Editor
Setting up a workflow means defining triggers and actions that will be executed based on these triggers.
Codemagic has a Flutter project tool called Workflow Editor. It provides a UI representation of your CI/CD. With Workflow Editor, configuring CI is quick and relatively simple. Workflow Editor allows you to avoid storing CI/CD parameters in the root of the remote repository, such as a .yaml file or a script. Although Workflow Editor may not provide the same level of customization. However, for most projects, especially smaller ones, this can be sufficient. If you are interested in configuring through a .yaml file, you can skip this section. We recommend following the sections sequentially and familiarizing yourself with the current section first to navigate the more advanced configuration effortlessly.
Build triggers
In this section of the Workflow Editor (referred to as WE), we configure the parameters for triggering code quality control operations (static code analysis, running tests, building the application for target platforms). For simplicity, we will refer to these operations as "build".
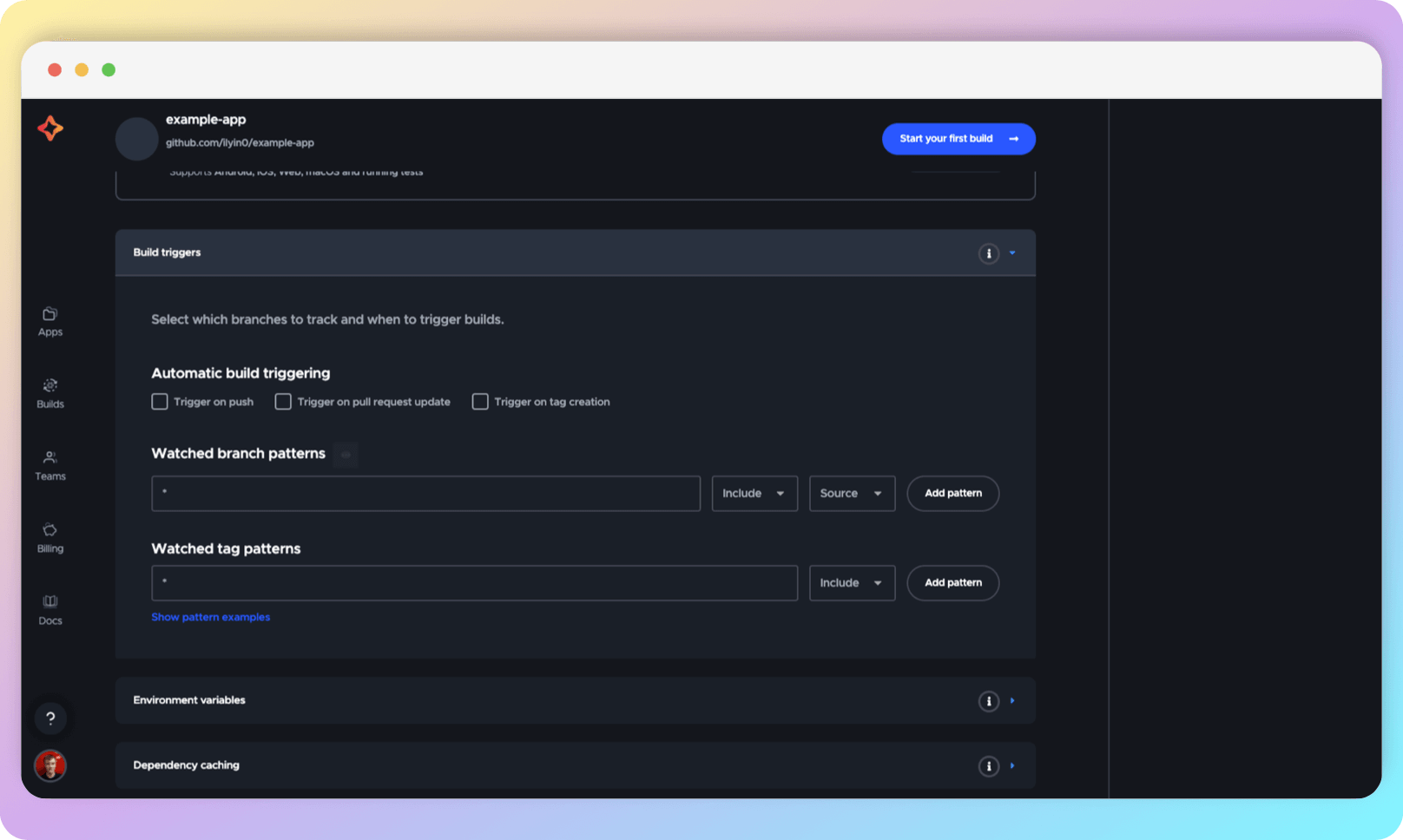
Most commonly, these operations need to be called on creating and updating Pull Requests (PRs), when making changes to the main repository branch.
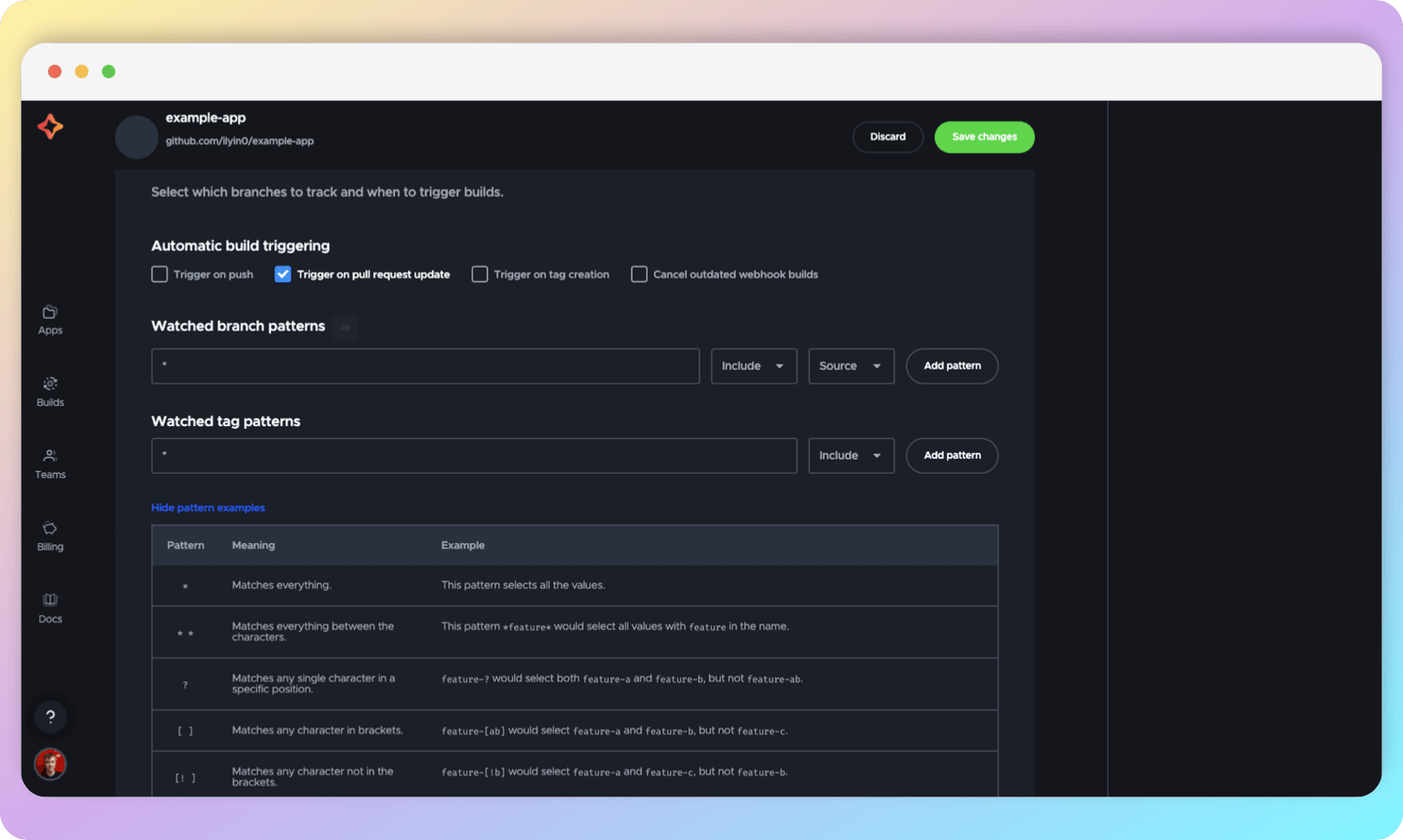
The other checkboxes signify the following:
- Trigger on push triggers a build after each push, such as creating a new branch;
- Trigger on tag creation triggers a build when tags are created;
- Cancel outdated webhook builds means that if a new build is triggered during the build process, the ongoing build will be terminated.
In the Watched branch patterns and Watched tag patterns fields, you can define names for branches and tags, respectively, for which builds will be triggered. This allows you to avoid unnecessary builds to speed up the development process (if limited by resources on the remote machine for running builds) or to save resources (if, for example, using a free version with a limited total number of build minutes per month).
Environment variables
In this section, you can add environment variables to customize the build. If you are unsure whether you need environment variables, you can leave this section unchanged.
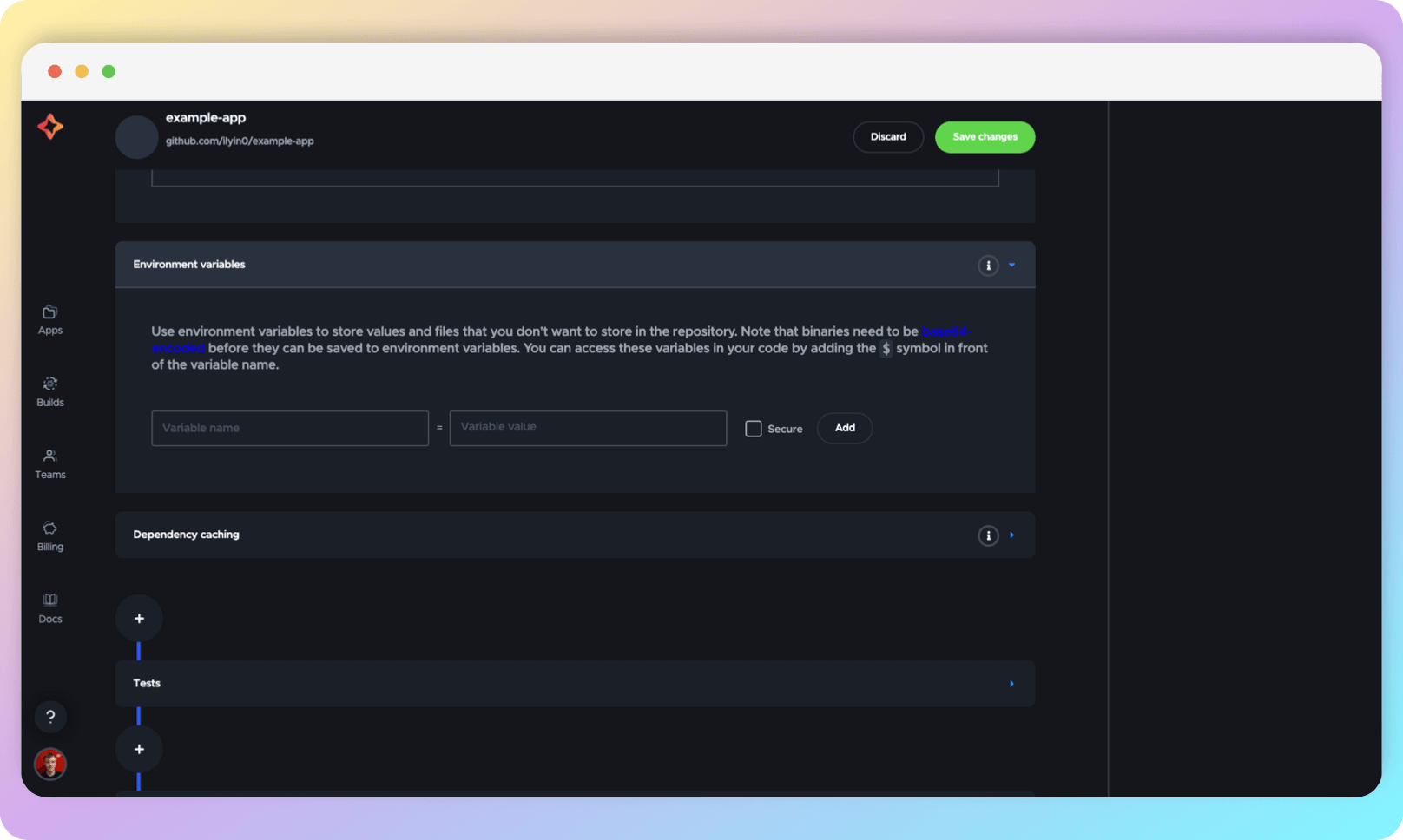
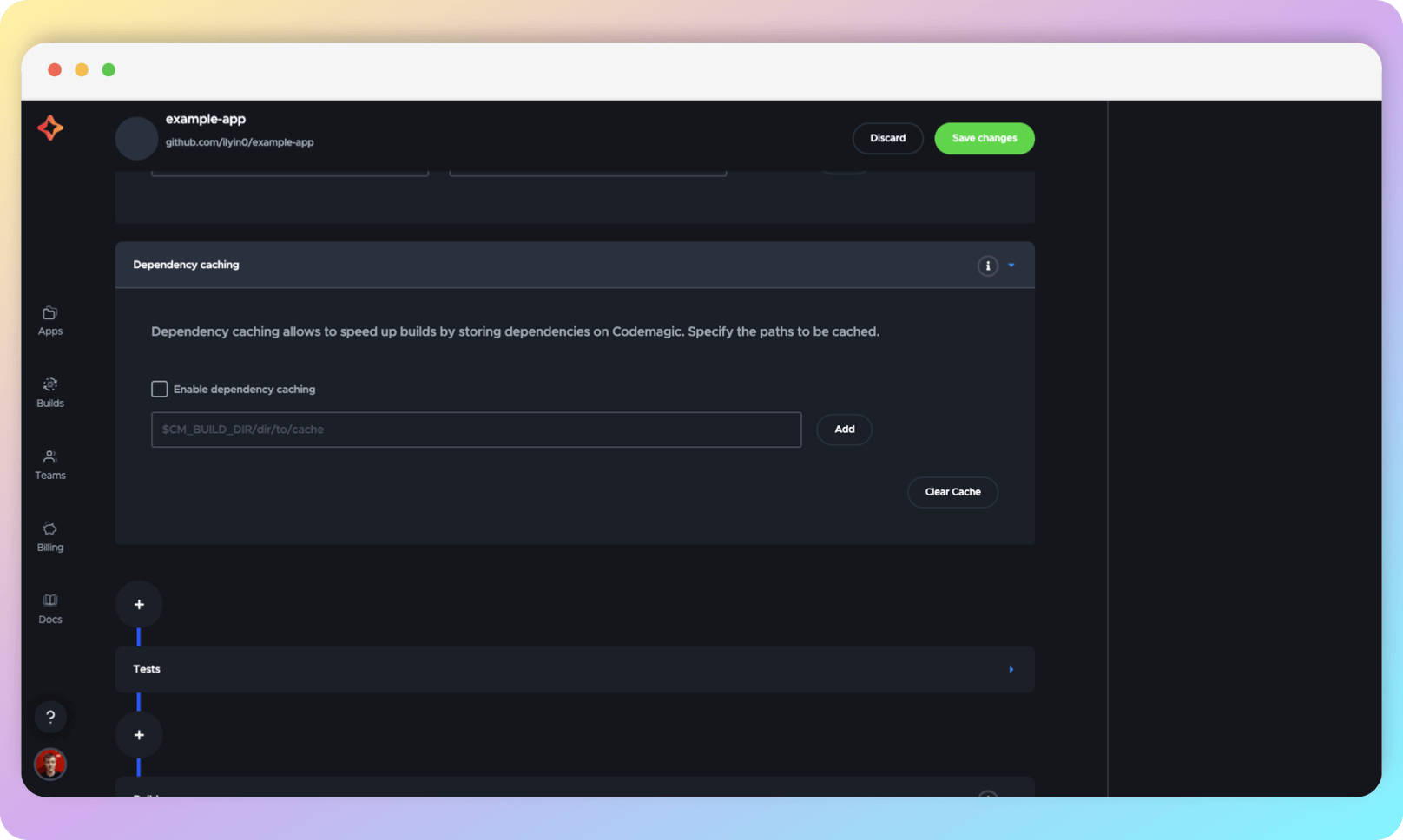
Dependency caching
In this section, you can specify which directories to cache for faster builds. In Flutter projects, the most common directory to cache is $FLUTTER_ROOT/.pub-cache (the Dart cache).
Tests
In this section, the code testing tools are configured. Enable Flutter analyzer enables static code analysis, Enable Dart Code Metrics is Codemagic built-in tool to quickly enable Dart Code Metrics (we recommend activating Dart Code Metrics in codemagic.yaml, after a quick setup).
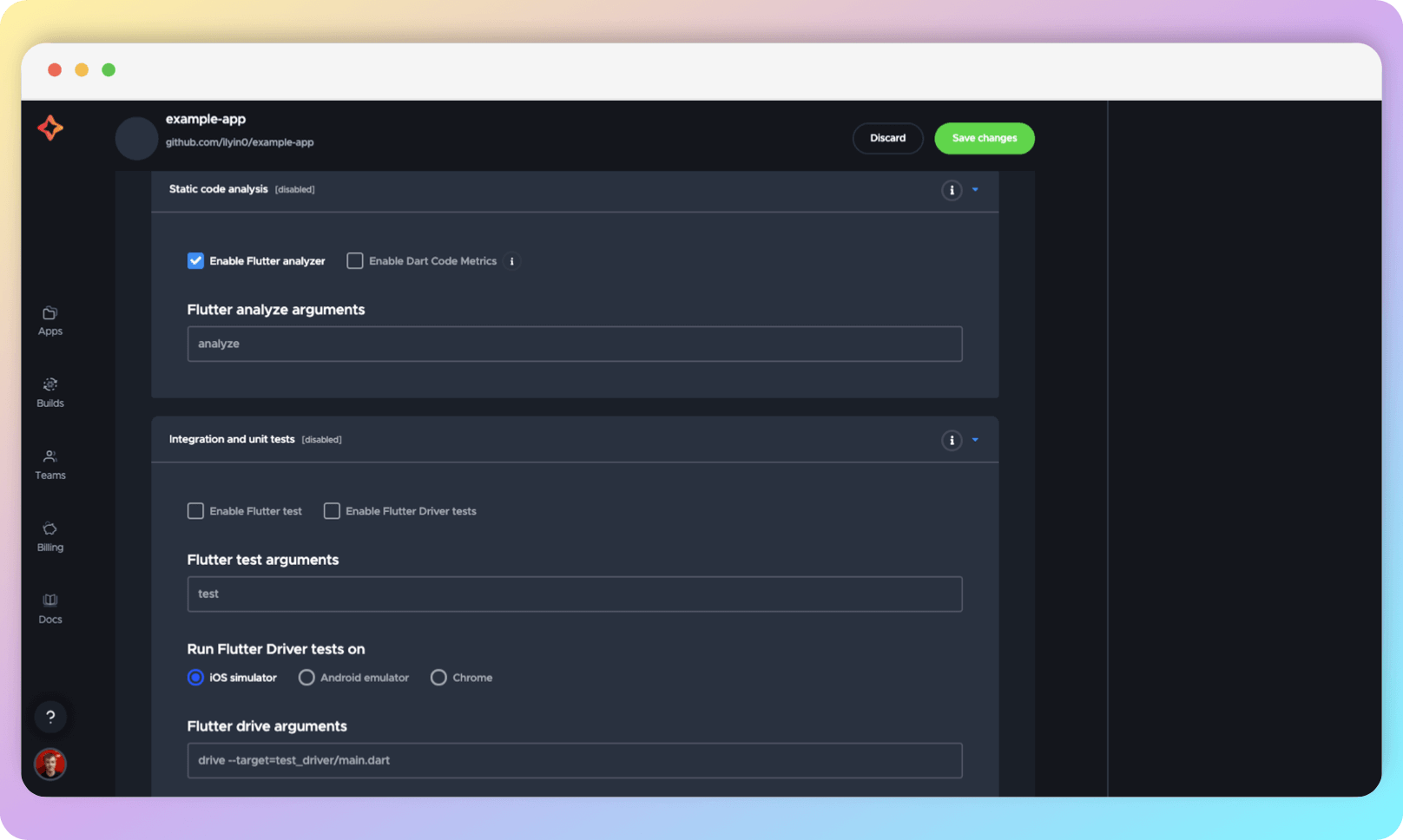
Enable Flutter test allows you to run unit tests, while Enable Flutter Driver tests is for UI tests (enable it if your project has them).
Build
In this section, you can configure the parameters for building your application. Building is necessary to ensure that the application runs on target platforms, as sometimes issues can arise even after passing all previous steps.
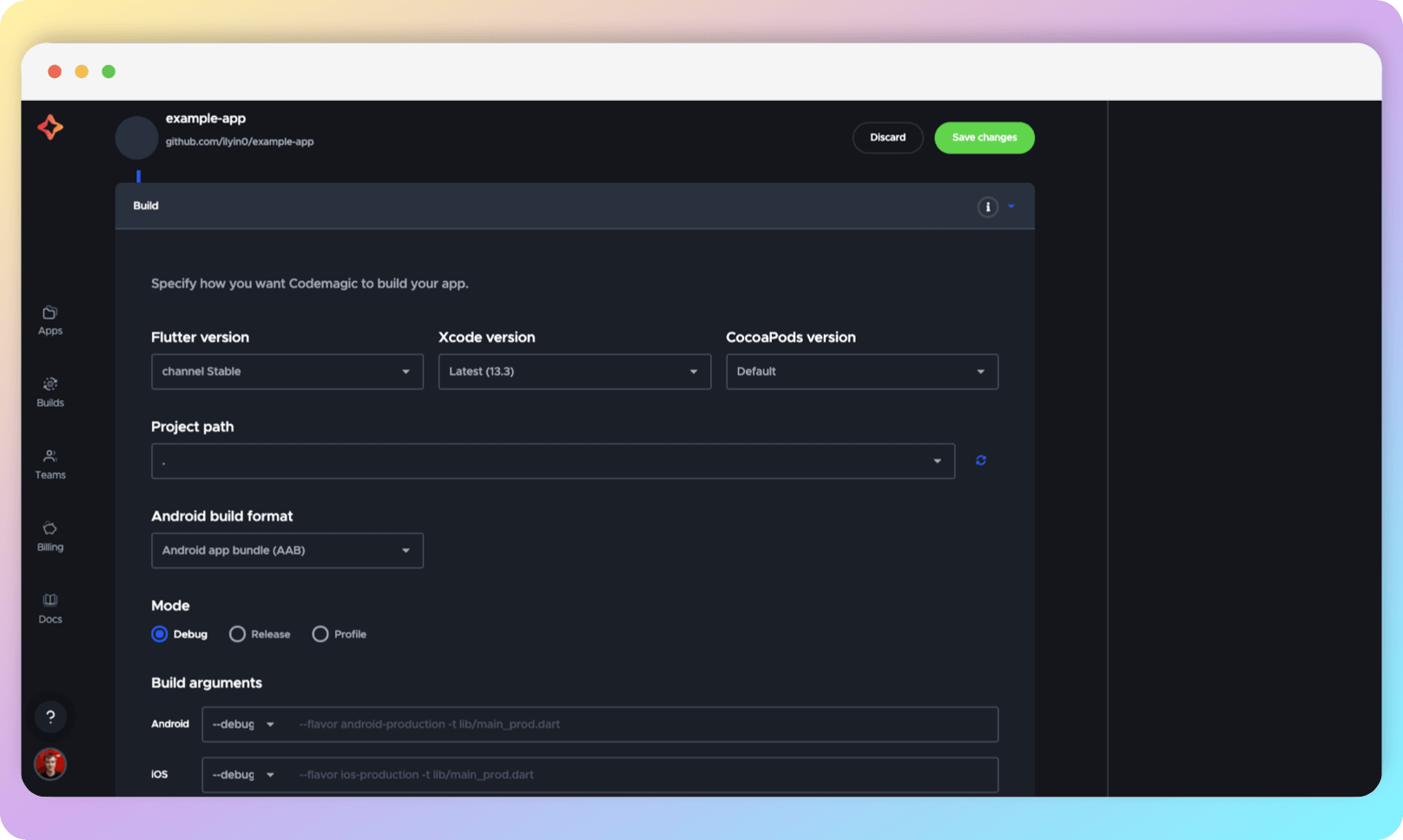
In the Project path, you can specify the path to the application, as it happens that several applications are stored in one repository at once. Otherwise, here you can select the build mode, build options for target platforms, Flutter, Xcode, and CocoaPods versions.
Notifications
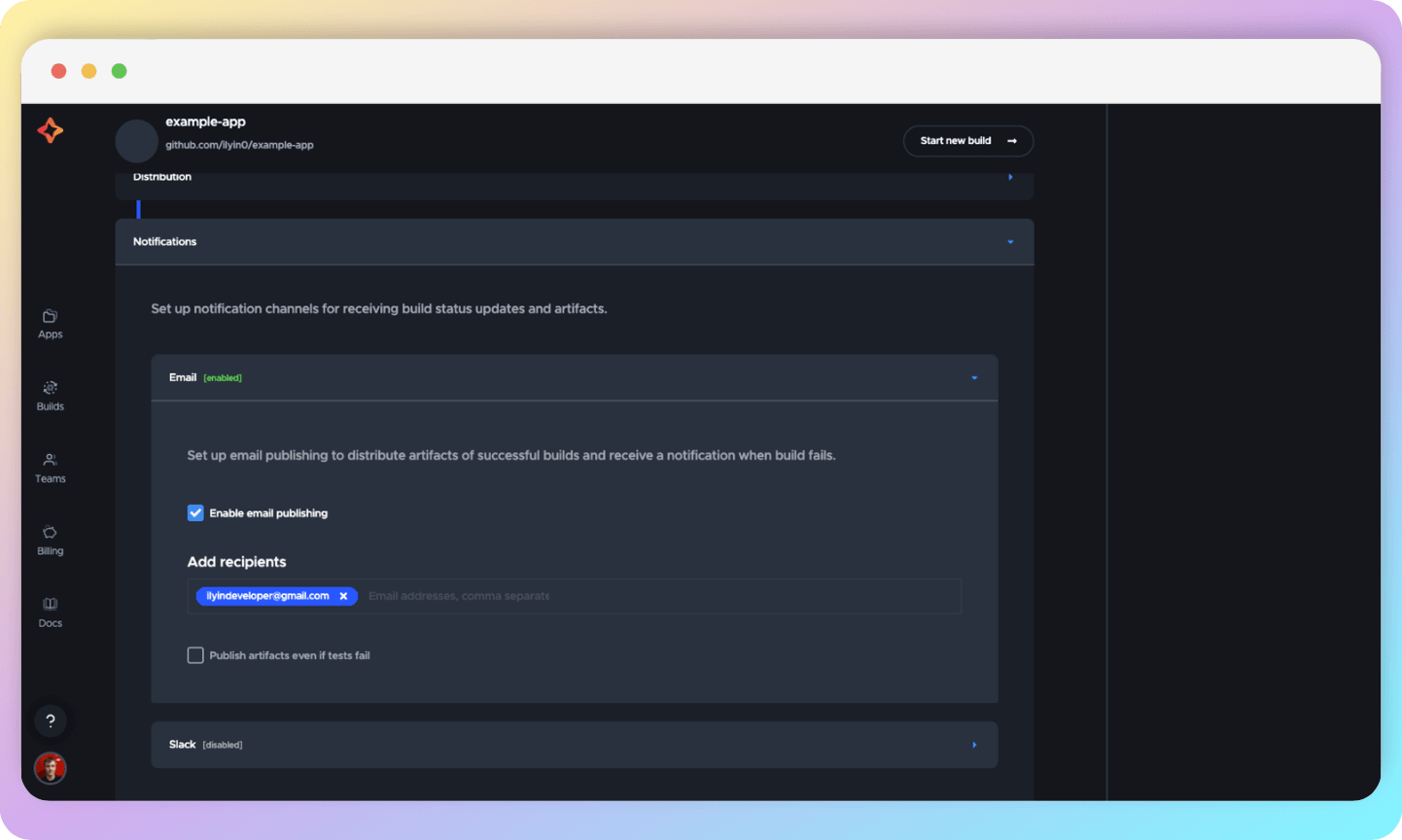
To track the success of a build, you can set up email notifications. To do this, go to the Notifications section at the bottom of the page and add/remove an email.
Build Run
To run the build, scroll up and click the Start your first build button.
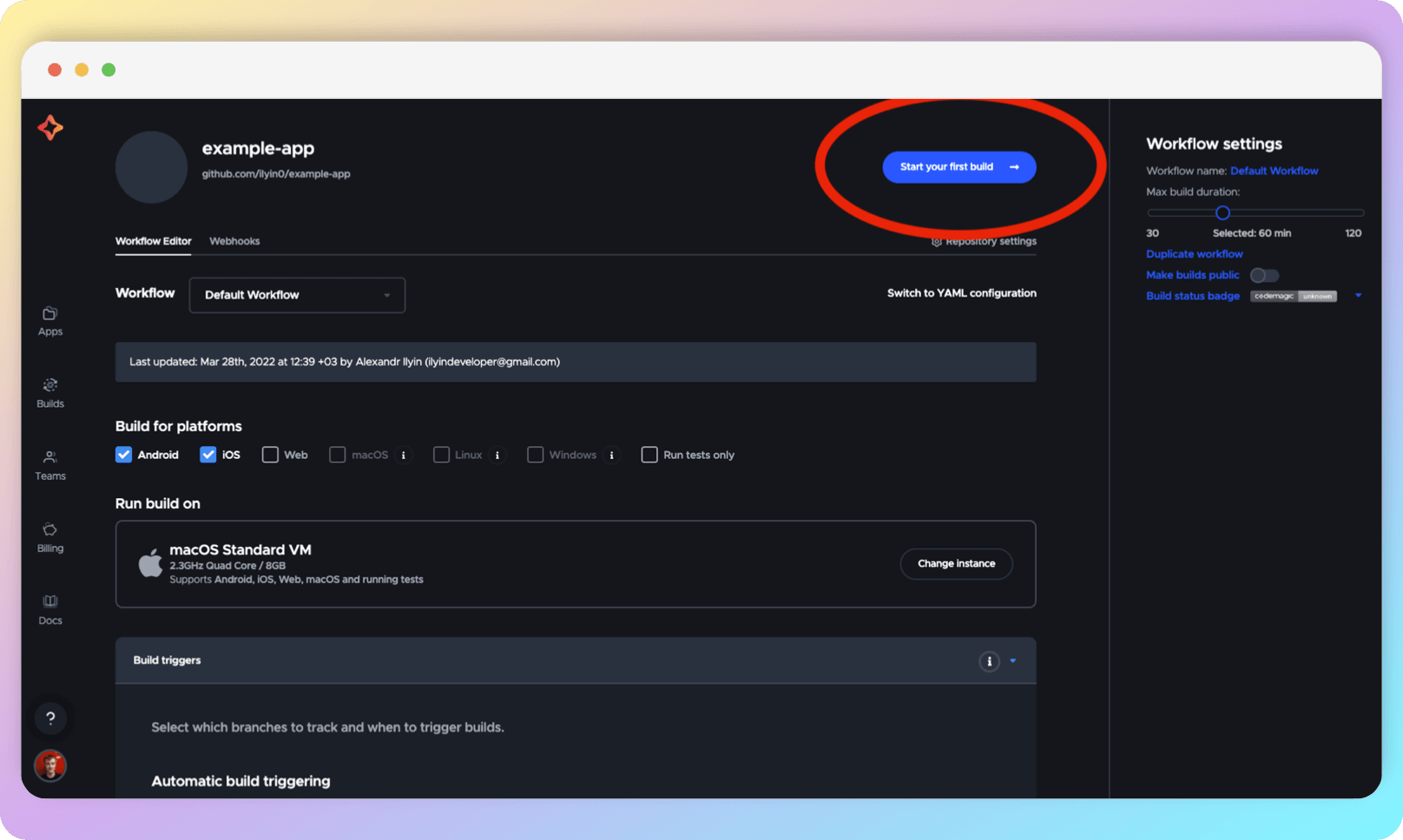
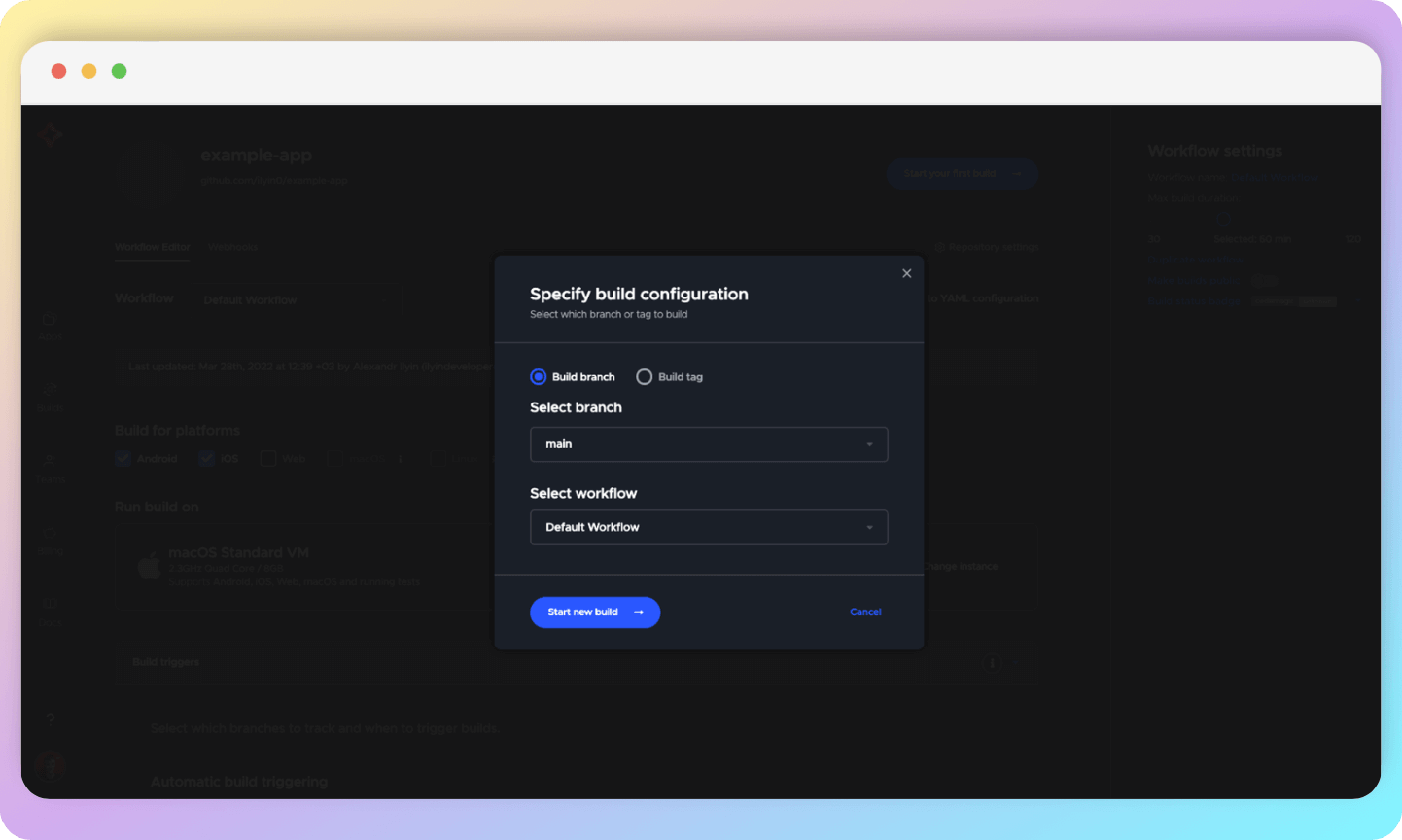
Moving forward, choose the branch for which the code is currently being built (this selection will not impact the workflow that was just configured) and select the workflow (Default Workflow by default).
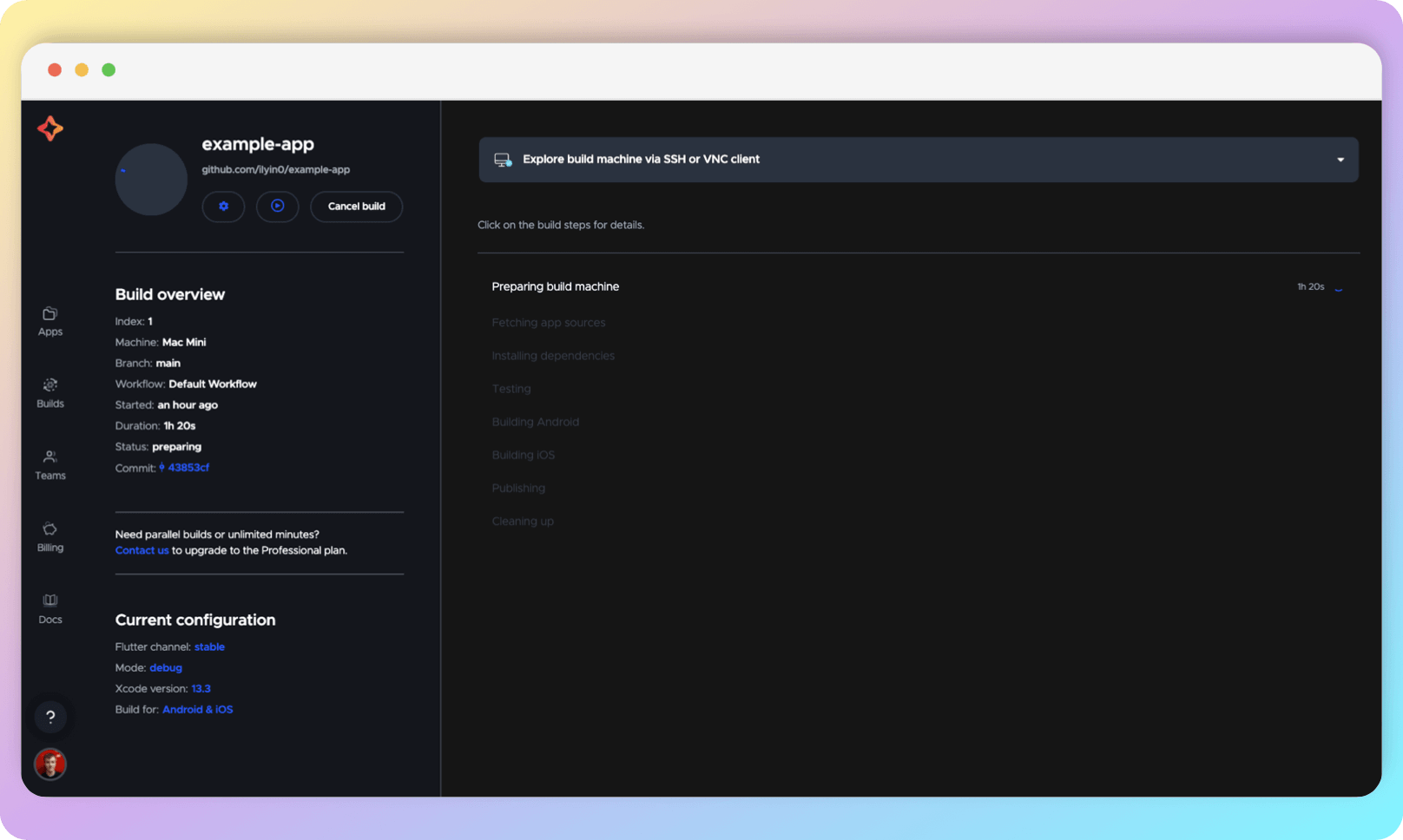
You will be taken to a screen that broadcasts the stages of the build in real time.
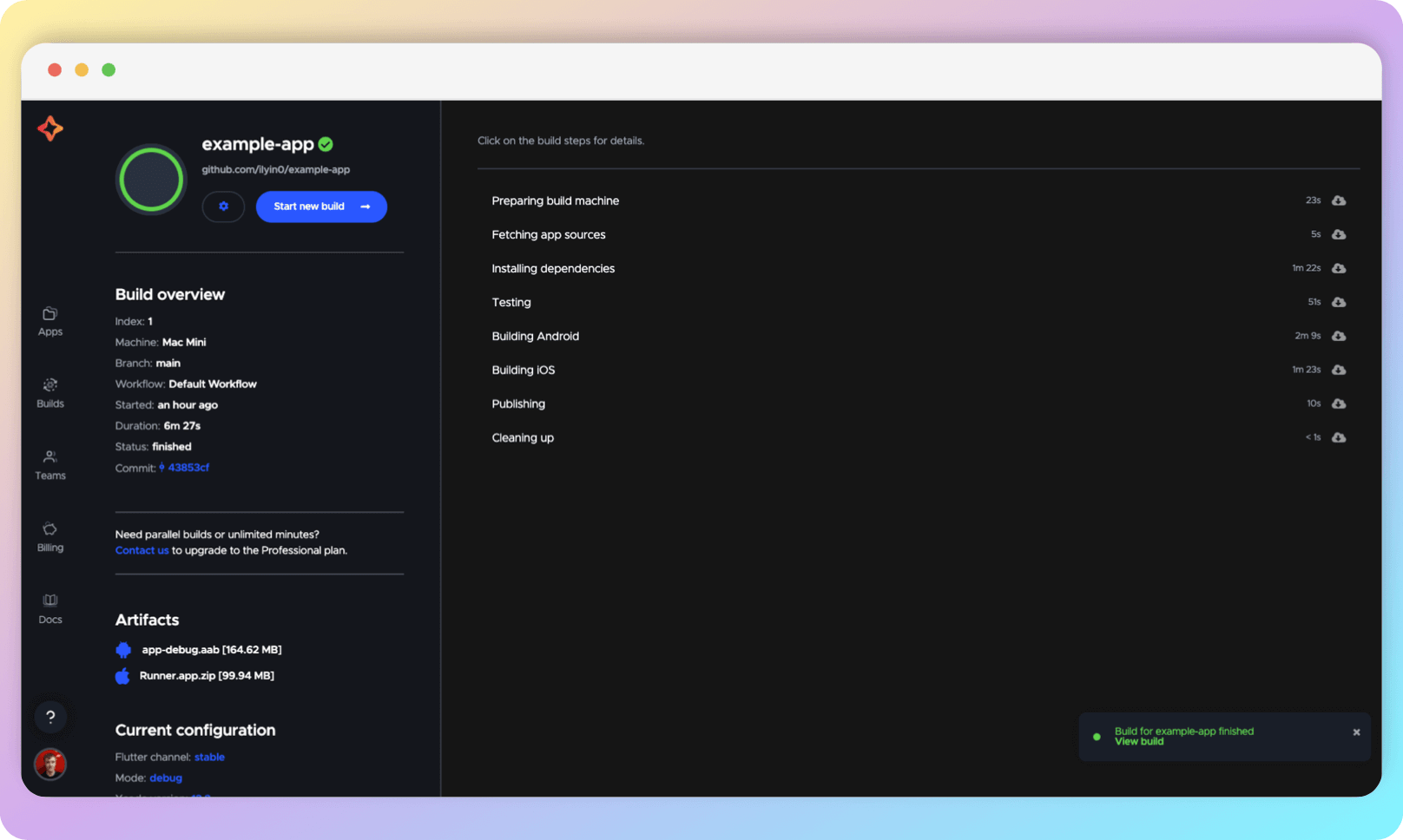
You don't have to keep this tab open and track the build steps yourself. If you have set up email notifications, you will receive an email with the result. Also, if you did everything right, you will see the results on GitHub. In the image below you can see a successful build.
Now try to create a PR and make sure the workflow works.
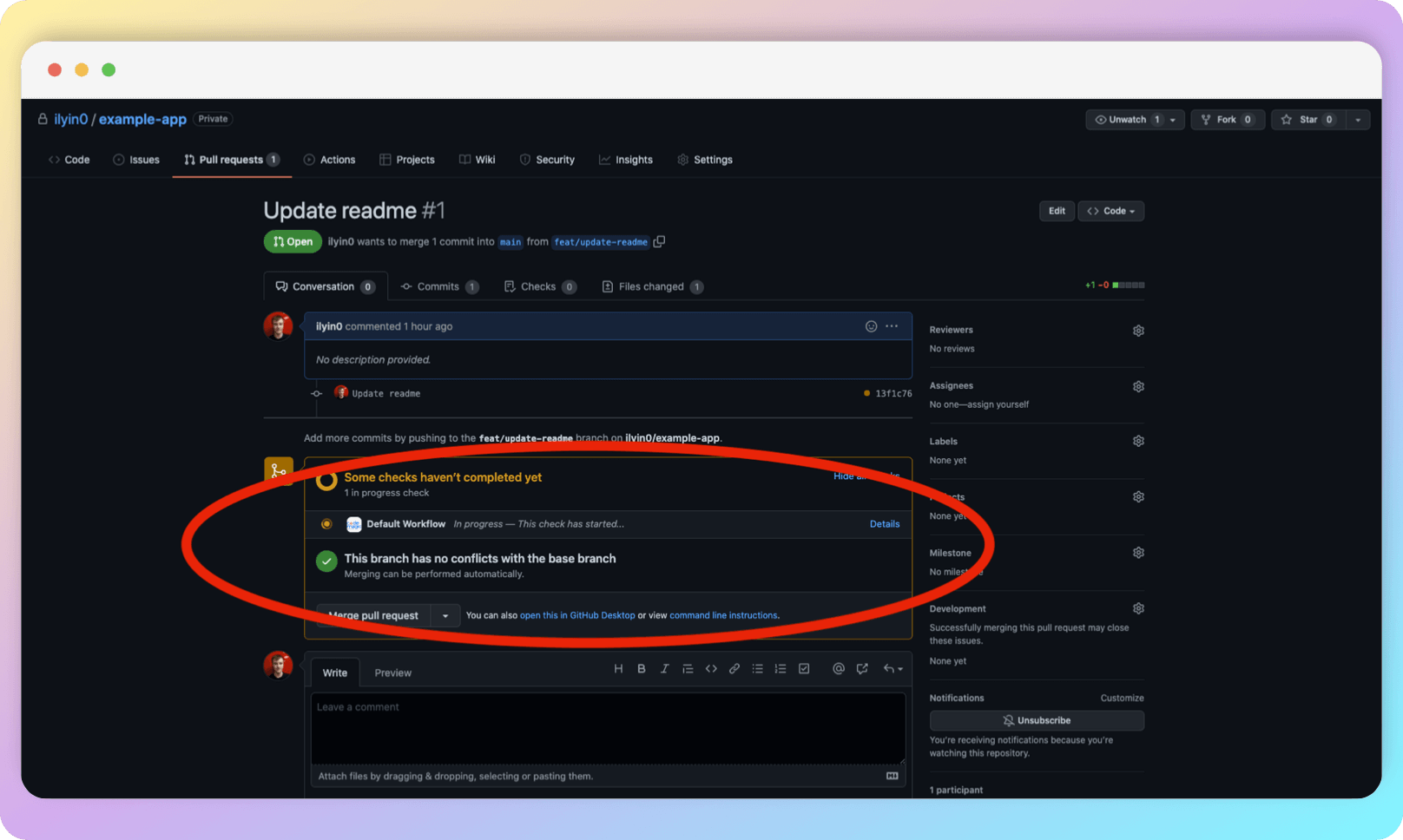
At this point, however, an unsuccessful build will not protect us from merging non-working code into the main branch. In the next section, we will set up the protection.
Main Branch Protection
In the project repository, go to Settings, select the Branches menu item and click Add rule opposite Branch protection rules.
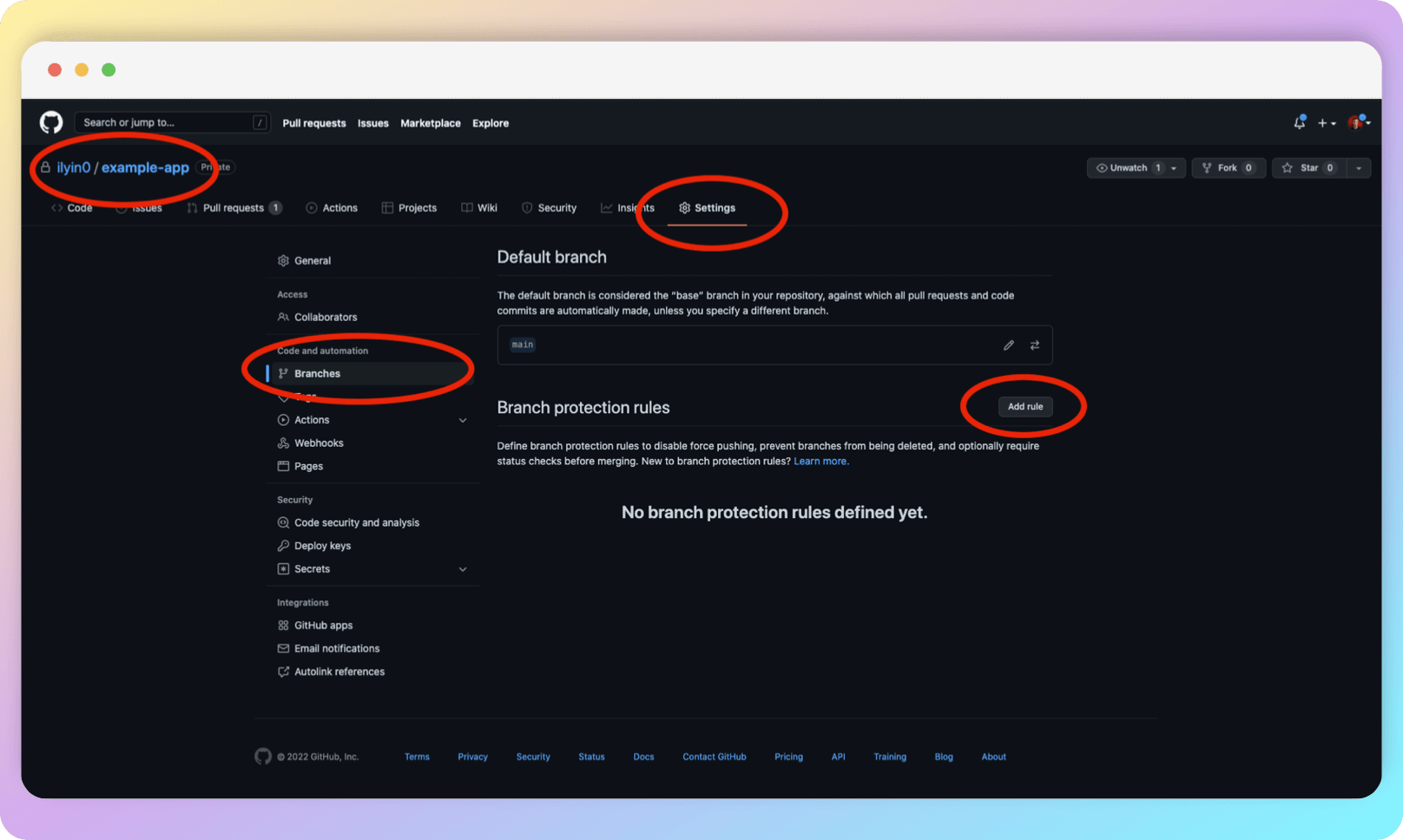
You will see a list with many parameters. For the purposes of this guide, we are interested in two rules:
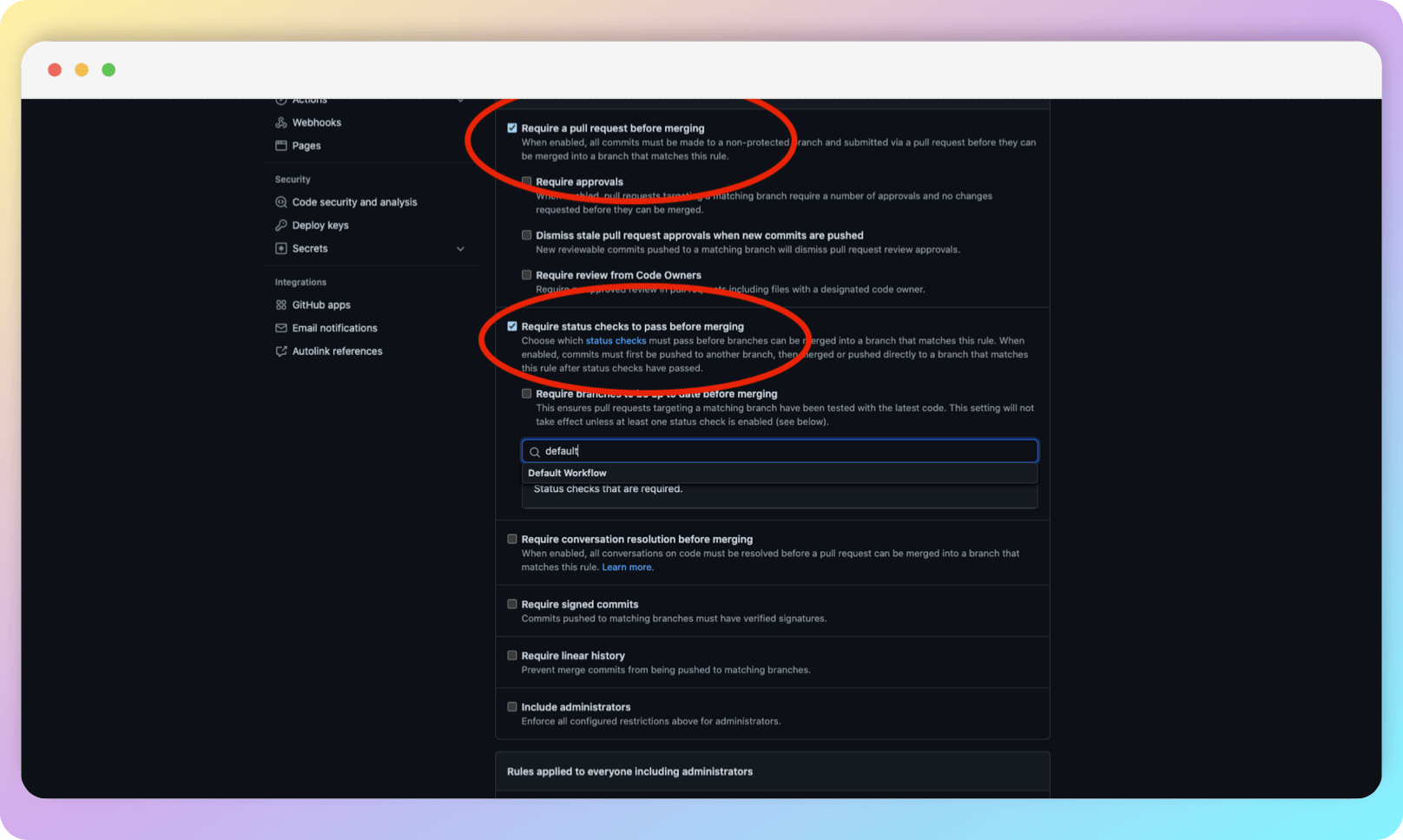
The first rule prohibits pushing into the protected branch directly, the second disables merge until the CI build is successful. In the line under the second rule, start typing the name of your workflow and select it. You may need to manually start a workflow at least once in order for a workflow to show up in search (we have done this before as part of this guide). After enabling the above options and selecting your workflow, go to the end of the page and click Create.
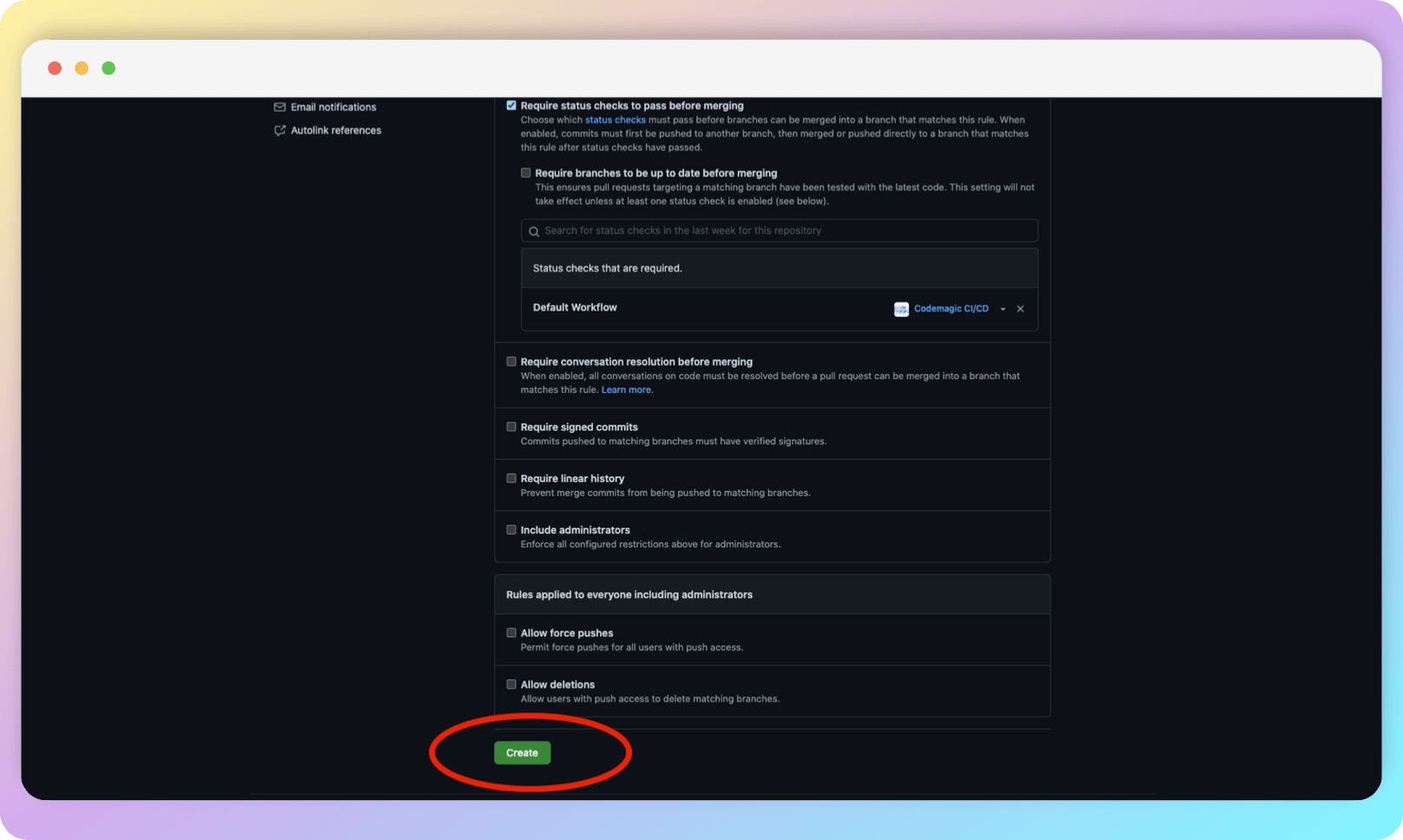
After that, during the build process or if the build fails, the PR merge will be unavailable.
You can now consider CI configured. If you need more fine-tuning, or if some parameters are not available in WE, we recommend reading on.
In Codemagic there is a second way to configure CI/CD (the first is WE). It consists of adding the configuration file codemagic.yaml in the root of the project. Since the connection between Codemagic and your project on GitHub is already established via webhook, a request is sent to Codemagic when there is any change in the repository. Codemagic reads codemagic.yaml from repository root and depending on configuration described in file it performs some actions (or not).
YAML Сonfiguration
To change the way you configure your workflow, scroll to the top of the WE configuration page and click Switch to YAML configuration.
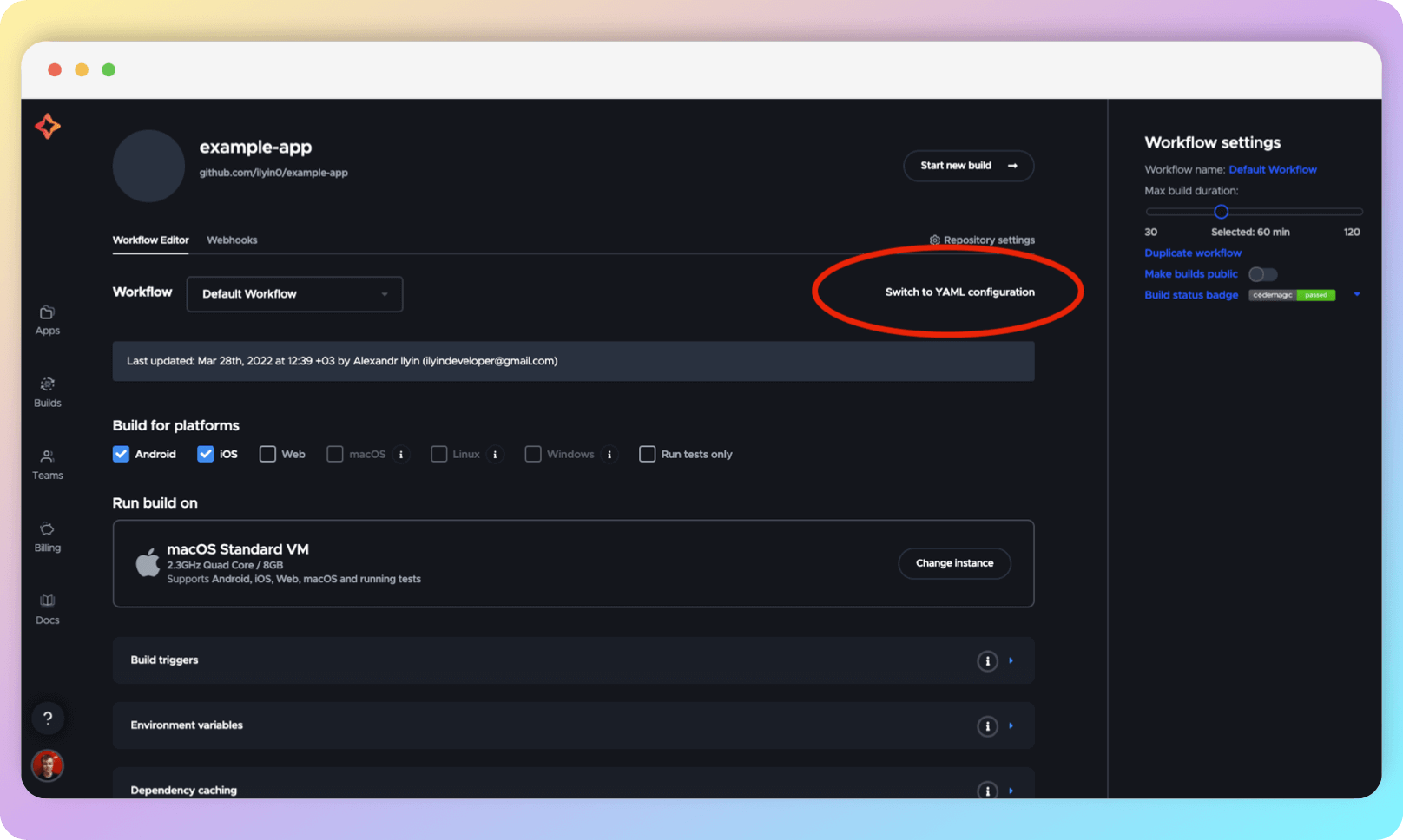
Codemagic will suggest that you export the current configuration. Be sure to do so.
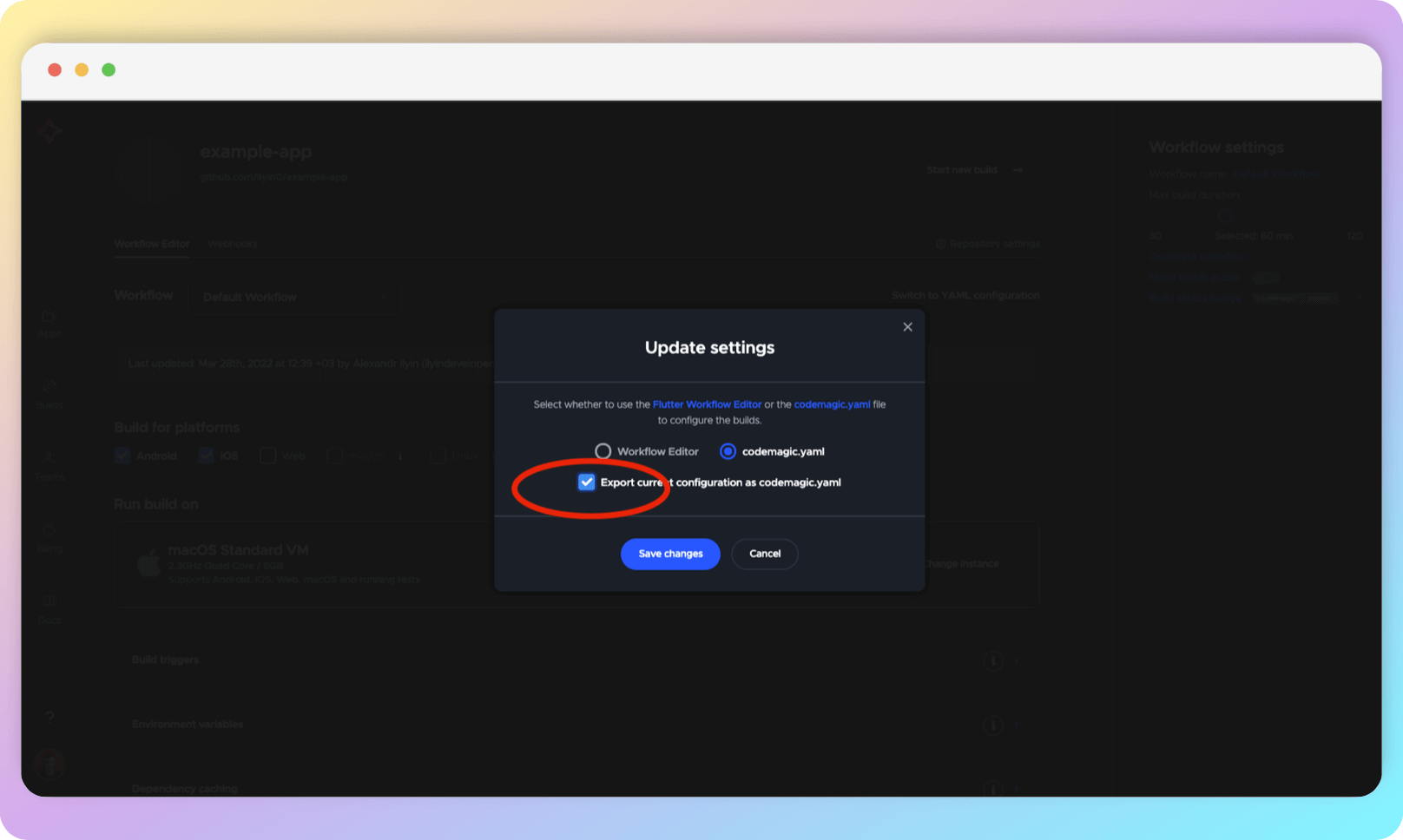
Click Save changes. The codemagic.yaml will be downloaded to your computer and you will be taken to the next page:
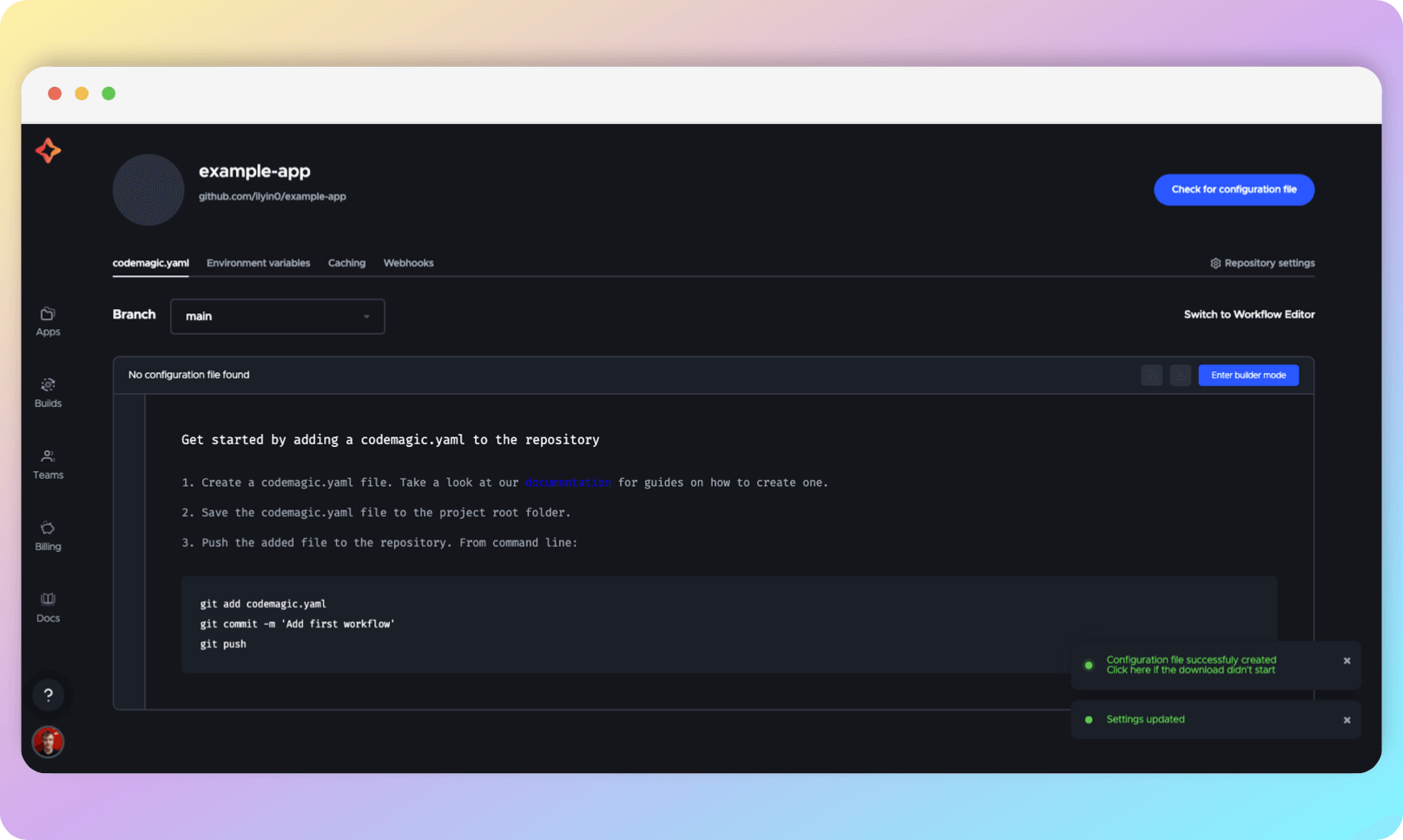
All that needs to be done next in order for CI to continue working is to push the codemagic.yaml file to the remote repository. When you do this, it will automatically pull up here as well.
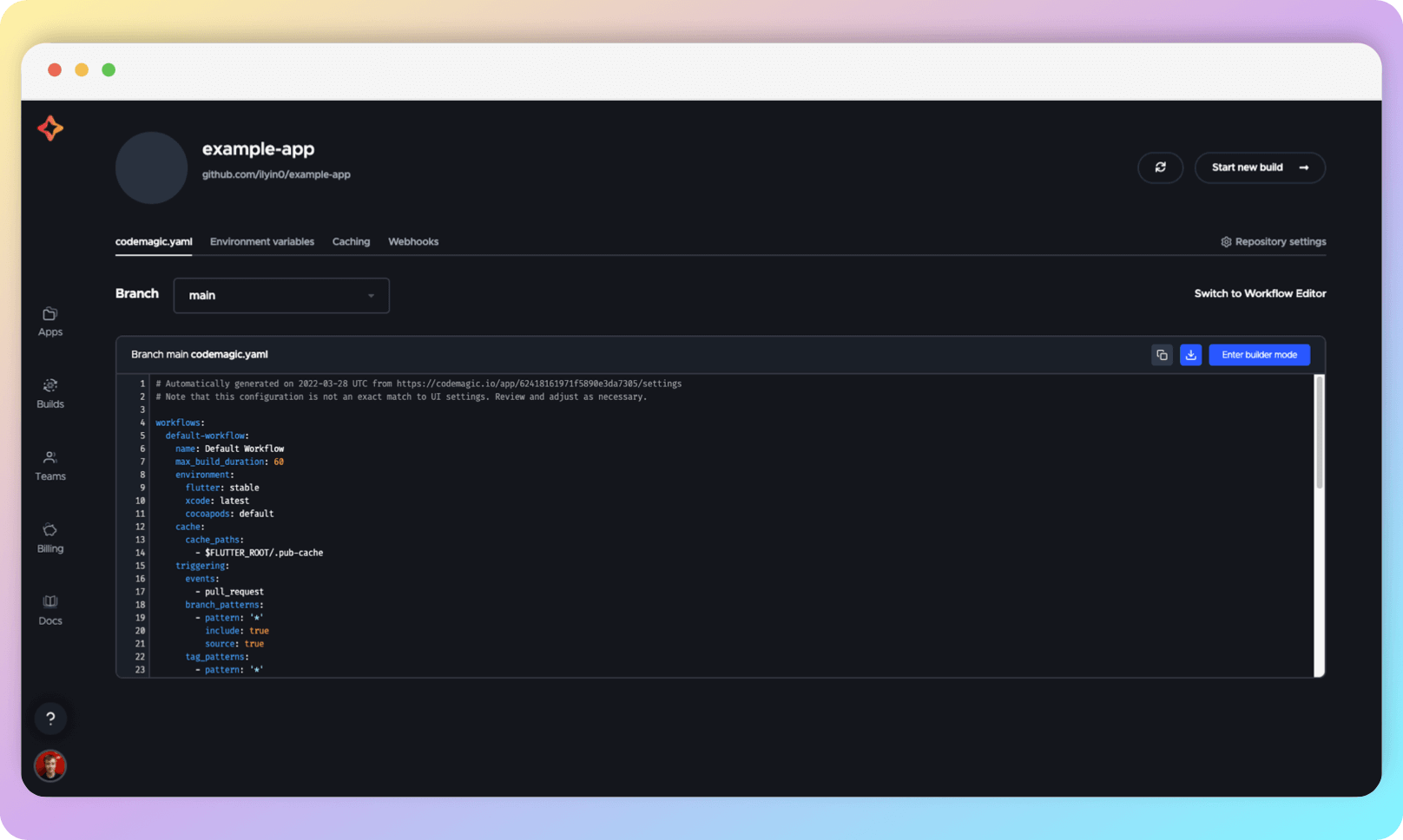
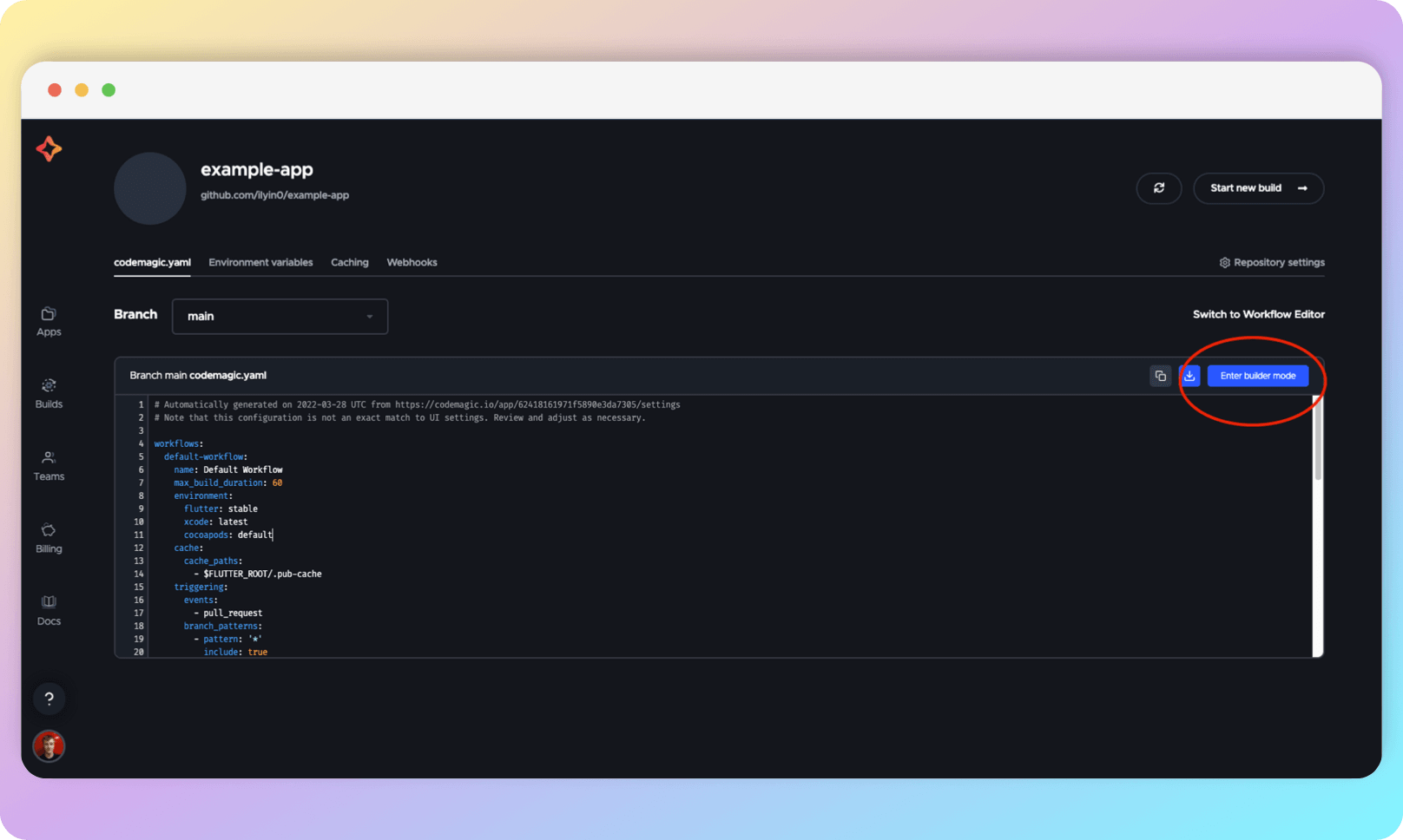
You can enter builder mode to see code examples for implementing various CI options.
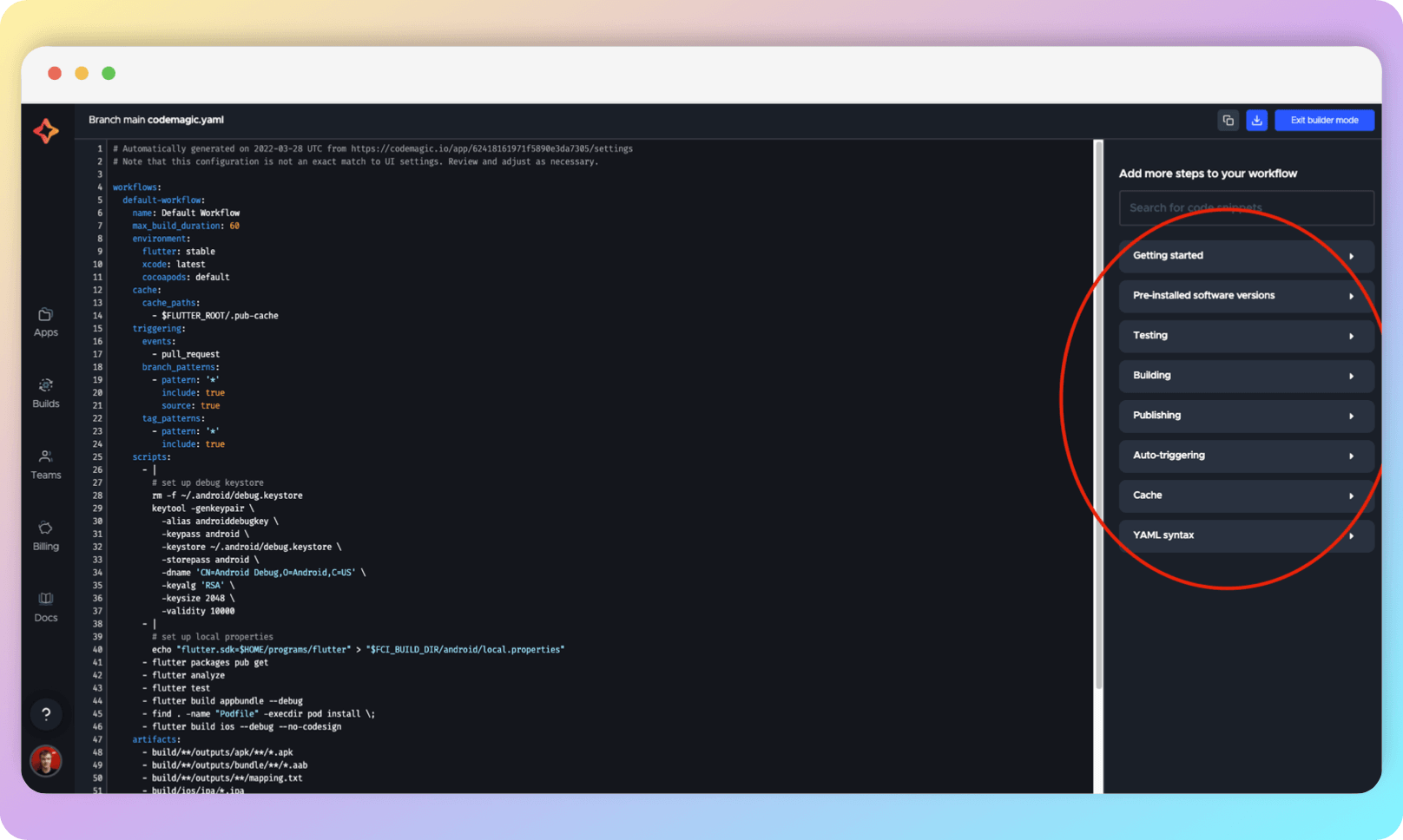
The advanced build configuration settings are described at this link.
Conclusion
This guide describes one of the many ways to set up CI for your project. Many of them are very similar, so once you understand one of them properly, it will be easier to interact with the others.
Codemagic is one of the easiest CI/CD tools for Flutter due to its graphical interface for configuring the workflow. We recommend using this method to quickly set up CI for your project.











